OSSC
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 AV inputs
- 3 AV outputs
- 4 Basic usage
- 5 Settings
- 6 Compatibility and special configuration
- 7 Remote control setup
- 8 Known issues / limitations
- 9 Firmware update
- 10 Firmware changelog and roadmap
- 11 Info for developers
Introduction
Open Source Scan Converter is a low-latency video digitizer and scan converter board designed mainly for connecting retro video game consoles and home computers into modern displays. It converts analog RGB/component video into digital format, and doubles (or triples) scanlines of a single frame if necessary to generate a valid mode for digital TVs or monitors.
The board and firmware was designed as a homebrew project mainly during 2015. The primary goal has been to make a scan converter with minimal latency and reasonable cost, which also can be built/assembled manually. Output image quality and features have also been important targets as long as they didn't contradict with primary goals.
Due to interest in the retrogaming community, both DIY kits and pre-assembled boards are released to public during early 2016. Firmware of the system is open source as the name suggests and new features can be expected after initial release.
If you're new to the device and scalers/processors in general, you may wish to start with the quick start guide here.
Features
- Detection and digitization of various analog SDTV/EDTV/HDTV/PC modes
- Linedouble-support for 240p, 480i, 288p, 576i, 384p
- Linetriple-support for 240p/288p with 4 different sampling modes
- Very low latency (less than 2 input scanlines)
- Fast "deinterlace" for 480i/576i
- Fast recover from input video mode change (e.g. 240p<->480i)
- All video processing done in RGB domain - no conversion to YCbCr
- Video and sync LPF for less-than optimal input signals
- Multiple inputs supporting various formats (see below)
- Full-range 24-bit RGB output through DVI/HDMI
- Emulated scanlines with configurable strength and position
- Configurable mask for overscan area
- Selectable sampling configuration for 480p input: DTV-480p or VGA 640x480
- Selectable CSC configuration for YPbPr source: Rec. 601 or Rec. 709
Board versions and availability
DIY kit
DIY kits contain a selection of special parts required for building a board. Common components such as SMD resistors/capacitors need to be ordered separately from e.g. Mouser. Kits are available to buy world-wide from VideoGamePerfection.com
Assembly instructions for v1.3 kit Assembly instructions for v1.5 kit
Pre-assembled board
Pre-assembled boards will be available to buy world-wide from VideoGamePerfection.com
More information & discussion
AV inputs
AV1 (RGB-SCART)
This input supports video in RGBS, RGsB (sync on green) and YPbPr formats. Composite video, luma or c-sync can be used as sync source with RGBS mode. External sync splitters / boosters are generally not required or recommended as there is built-in sync filter & separator in the ADC frontend. The sync input has 75ohm termination, so TTL-level c-sync should not be connected directly there in order to avoid unnecessarily stressing source console and/or scanconverter. A 470ohm series resistor on the console side of the cable generally is a good solution when using cables which are wired for TTL-level c-sync output of a console. Video inputs also have standard 75ohm termination, so arcade boards may need extra resistors on the cable when connected directly without using a SuperGUN.
AV2 (Component)
3xRCA input supports for component video (YPbPr) and RGB (RGsB format).
AV3 (VGA)
VGA/HD-15 input supports video in RGBHV, RGBS (pin 13), RGsB and YPbPr formats. RGBHV and RGBS modes require clean TTL-level sync signals and cannot extract sync from composite/luma. VGA input is best suited for high-quality input sources as video LPF functionality is limited (SCART and Component inputs are routed through a dedicated LPF chip). Therefore, it is generally recommended to connect older consoles and arcade boards to other inputs.
AV outputs
HDMI (DIY boards)
DIY boards contain a HDMI connector which is used to transmit video data in 24bit RGB format. Digital audio output is not available in current boards. Currents up to 200mA can be safely supplied via power pin to external devices such as active cables.
DVI-D (pre-assembled boards)
Due to HDMI licensing requirements and fees, pre-assembled boards come with DVI-D connector. Functionality is otherwise similar, and it is possible to use a DVI-to-HDMI cable or adapter to connect to a HDMI display. Analog output pins of DVI are not used, so it is not possible to connect to a VGA monitor via a passive DVI-to-VGA cable or adapter (an active adapter is required instead).
AV1 audio
Analog audio from SCART input is bypassed to a 3.5mm stereo output jack next to video output connector.
[Optional] Digital audio output
Borti4938 has created an add-on board that implements audio digitization and integration into HDMI output, which neither are natively supported by OSSC. Both SCART input and 3.5mm connector (normally output) can be used as audio input, but it is highly recommended to have only either one of those connected at time since they are wired together internally.
All OSSC boards are compatible with the mod (with -aud firmware), but required installation effort depends on OSSC/mod PCB versions. More information is found at github page of the mod.
Basic usage
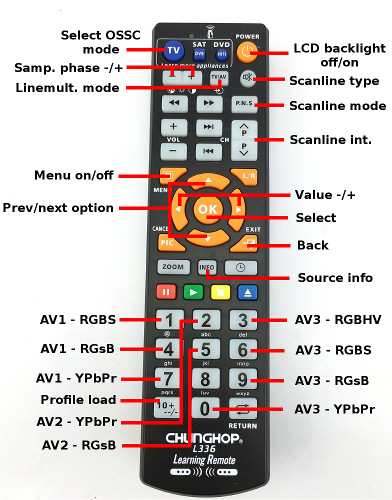
Remote control
The OSSC is available with a pre-programmed infrared remote. This is optional, and can be replaced with a suitable learning remote if desired (see Remote control setup).
- 0-9: Selects AV source and input format. See remote picture on the side for reference.
- MENU: Activates/deactivates menu at on-board character LCD display
- OK: Selects sub-menu or function
- BACK: Returns to previous menu level or from info page to normal source display page
- UP/DOWN: Selects next/previous menu option
- LEFT/RIGHT: Option value -/+
- INFO: Displays extra information on video source processing: VMod=selected output mode for the current source. LO=total number of lines output by FPGA. VSM=vsync generation mode (0=directly from source, 1-2=FPGA modified)
- LCD_BACKLIGHT: Turns on-board character LCD backlight off/on
- SCANLINE_MODE: Hotkey for selecting next "Scanlines" option value
- SCANLINE_TYPE: Hotkey for selecting next "Scanline type" option value
- SCANLINE_INT+/-: Hotkeys for adjusting scanline strength
- LINEMULT_MODE: Hotkey for toggling between linedouble and linetriple
PCB buttons
- BTN0: Next input/mode
- BTN1: Select between scanlines off/auto/manual
Status LEDs
- Green: Power on. Light off when IR remote code detected
- Red: Unstable sync when alight.
Settings
Video in proc
Video LPF
Video low-pass filter. Filters out high-frequency noise on video, and can reduce jitter when sampling clock does not match input video dot clock rate (e.g. older consoles in linedouble mode). NOTE: The last 3 settings are not effective with VGA input in RGBHV/RGBS mode.
- Auto: Suitable LPF is automatically selected based on input source and video mode [default]
- Off: LPF is disabled.
- 95MHz (HDTV II): 95MHz bandwidth – suitable for 1080p
- 35MHz (HDTV I): 35MHz bandwidth – suitable for 720p
- 16MHz (EDTV): 16MHz bandwidth – suitable for 480p etc. EDTV formats
- 9MHz (SDTV): 9MHz bandwidth – suitable for 240p, 480i etc. SDTV formats
YPbPr input Color Space
Controls YPbPr->RGB colorspace conversion coefficients.
- Rec. 601: Input is assumed to be in Rec. 601 format, which is generally true for SD video [default]
- Rec. 709: Input is assumed to be in Rec. 709 format, which is generally true for HD video
R/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb offset
Adjusts Red/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb channel offset (brightness)
- 0-255: [default=127]
R/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb gain
Adjusts Red/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb channel gain (contrast)
- 0-255: [default=26]
Sampling opt.
Sampling phase
- 0-347 deg: Selects the phase of regenerated pixel clock (=position where each sample is taken). When output rate matches the input DAC rate (PC graphics modes, newer consoles, 2 last linetriple modes), it is important to adjust sampling phase for optimal quality. This setting should be adjusted only after adjusting sync and video LPF since they can alter the relative position of video and sync signals. [default=180deg]
480p in sampler
Controls the sampling mode when 525-line progressive signal (“480p”) is detected at input
- Auto: “VGA 640x480”-mode is selected when the signal comes from RGBHV input. “DTV 480p”-mode is selected with all other inputs [default]
- DTV 480p: Input is sampled at 858 samples per line, typically associated with 720x480 mode (CEA-861 spec.) used by DTV/DVD equipment and newer game consoles. This option forces the sampling mode for all inputs, which may be required for optimal image quality when e.g. Dreamcast with a VGA module is connected to RGBHV input.
- VESA 640x480@60: Input is sampled at 800 samples per line, typically associated with VESA 640x480@60Hz mode used by PCs. This option forces the sampling mode for all inputs.
Advanced timing tweaker
Allows manually tweaking sampling parameters. Results greatly depend on displays - generally only position (backporch) adjustments are highly compatible. Efficient use requires knowledge of input and output hardware connected to OSSC. Video mode to edit (default is current mode) is selected via LEFT/RIGHT keys, after which tweaker is accessed via OK key.
Horizontal samplerate
Sets how many samples ADC take each scanline (=between 2 hsync signals). Mainly usable for console-specific fine-tuning in 320x240 / 256x240 optim. modes.
Horizontal sync length
Sets the length of assumed horizontal sync (also becomes output horizontal sync length). Usually no need to modify.
Horizontal/Vertical active length
Sets the area which is marked as active in output signal. Allows adjusting image size on compatible displays.
Horizontal/Vertical backporch length
Sets the assumed backporch length, which basically adjusts image position.
Sync opt.
Analog sync LPF
Low-pass filter selection for analog sync signals (SCART and component inputs plus VGA input in RGsB mode). Required if there is noise or glitches on the sync line.
- Off: Sync is processed unfiltered [default]
- 33MHz: Lowest filtering
- 10MHz: Medium filtering
- 2.5MHz: Heavy filtering – recommended only if the above settings are not sufficient for stable sync, since excessive LPF can cause image jitter.
Analog sync Vth
Sets the sync slicer threshold. May help with dropouts as the last resort - sync LPF and coast settings should be tested through first.
- 0-350mV: threshold voltage. [default=124mV]
Hsync tolerance
Sets tolerance for hsync period variation outside of vsync. Needs to be increased from default to allow detection of some consoles like certain Neo Geo models. H-PLL coast also needs to be increased to enable stable output with these problematic sources.
- 0-39.2us: max. allowed period variance. [default=0.92us]
Vsync threshold
Sets delay threshold for extracting vsync from csync. The value should be higher than hsync length but lower that actual vsync length. Useful setting for Taito F2/F3 arcade boards
- 1.5-30.7us: delay threshold. [default=10.4us]
H-PLL Pre-Coast
Defines when PLL coast (current freq. freeze) is activated. Higher than default value needed with some sources (e.g. MD) for stable sync.
- 0-5 lines: Number of scanlines before vsync at when coast is activated. [default=1]
H-PLL Post-Coast
Defines when PLL coast (current freq. freeze) is deactivated. Higher than default value needed with some sources (e.g. MD) for stable sync.
- 0-5 lines: Number of scanlines after vsync at when coast is deactivated. [default=0]
Output opt.
240p/288p lineX3
Controls whether 240p/288p is linetripled instead of standard linedouble. NOTE: resulting modes do not have the same parameters (total lines, pixels per line) as standard CEA 720p mode, so they are generally accepted only by monitors and not by many consumer TVs.
- Off: 240p/288p is linedoubled, resulting to 480p output. [default]
- On: 240p/288p is linetripled, which results to 720p output.
Linetriple mode
Controls the sampling and pixel clock multiplication mode for linetriple.
- Generic 16:9: Uses full horizontal sample rate without pixel multiplication, resulting to fully utilized 1280x720/864 output (16:9 aspect). Useful if connected to a CRT via DVI->VGA converter. [default]
- Generic 4:3: Uses 3/4 of full horizontal sample rate without pixel multiplication, resulting to 960x720/864 effective area of 1280x720/864 output (4:3 aspect).
- 320x240 optim.: For advanced users only - requires clock and phase adjustments. Uses a sampling rate which matches the DAC rate of 426 dots per line used by some classic consoles (e.g. several PSX games) in 320x240 mode, resulting to pixel-perfect digitization. Output is pixel-multiplied by 3 in horizontal direction, resulting to 960x720 effective area of 1280x720 output. Note: If picture jitters when this mode is selected, adjust sampling phase until sweet spot is achieved.
- 256x240 optim.: For advanced users only - requires clock and phase adjustments. Uses a sampling rate which matches the DAC rate of 341 dots per line used by various classic consoles (e.g. NES, SNES) in 256x240 mode, resulting to pixel-perfect digitization. Output is pixel-multiplied by 4 in horizontal direction, resulting to 1024x720 effective area of 1280x720 output. Note: If picture jitters when this mode is selected, adjust sampling phase until sweet spot is achieved.
480p/576p lineX2
Controls whether EDTV sources are linedoubled and 2x integer scaled horizontally
- Off: 480p/576p sources are output as is. [default]
- On: 480p/576p sources are linedoubled and 2x scaled horizontally. With 480p sources, resulting output mode is 1440x960 or 1280x960 depending on 480p in sampler setting. With 576p sources, resulting output mode is 1440x1152. NOTE: these output modes are best compatible with CRTs/PC monitors/capture cards - not many flat-panel TVs accept / show them correctly.
480i/576i passtr
Controls whether interlaced SDTV sources are passed to the display as-is without linedoubling
- Off: 480i/576i sources are linedoubled, resulting to most compatible and lag-free picture. [default]
- On: 480i/576i sources are just digitized and passed to display. Deinterlacing will be handled by display, resulting to higher quality picture at the price of added latency. NOTE: several PC monitors do no accept interlaced sources.
TX mode
Sets the output TX mode.
- HDMI: auxiliary HDMI packets are sent along with video data, such as Infoframes which indicate color settings (RGB, full-range).
- DVI: Only video data is sent to the display. Required if target display does not support HDMI.
Initial input
Sets the input which is automatically activated when device is powered on. Test pattern is diplayed regardless of the setting until sync is detected on the respective input.
Post-proc.
Scanlines
Controls whether emulated scanlines are drawn on top of the picture
- Off: No scanlines drawn [default]
- Auto: Horizontal scanlines are drawn for 240p/288p sources, alternating scanlines are enabled for 480i/576i, no scanlines for other sources
- Manual: Scanlines are drawn for every source according to "Scanline type" option
Scanline str.
- 6-100%: Strength of the emulated scanlines [default=6%]
Scanline type
- Horizontal: Scanlines drawn on every other (digitize & linedouble modes) or every third (linetriple) output line
- Vertical: Scanlines drawn on every other output column
- Alternating: Horizontal scanlines are drawn for every other output line so that id toggles at field change. Useful with interlaced sources to reduce flicker.
Scanline alignment
- Top: Scanline is drawn on top position of every group of output lines formed from a single input line. [default]
- Bottom: Scanline is drawn on bottom position of every group of output lines formed from a single input line.
Horizontal mask
- 0-63 pixels: Controls the size of a mask (black border) generated around the picture in horizontal direction (1-pixel steps). Can be used to mask areas which would get hidden in the overscan region of CRT TVs. [default=0]
Vertical mask
- 0-63 pixels: Controls the size of a mask (black border) generated around the picture in vertical direction (1-pixel steps). Can be used to mask areas which would get hidden in the overscan region of CRT TVs. [default=0]
Audio options (available in -aud firmware)
Down-sampling
- 2x (fs = 48kHz): Downsample 24bit/96kHz audio signal from audio ACD to 24bit/48kHz for best compatibility. [default]
- Off (fs = 96kHz): Do not downsample digitized audio signal.
Swap left/right
- Off: Do not swap audio channels. [default]
- On: Swap left/right audio channels.
Fw. update
See the dedicated section on the bottom.
Reset settings
Resets settings to defaults (use following option subsequently to save defaults on flash)
Save settings
Saves settings (all previous and remote control config) to flash.
Compatibility and special configuration
We encourage the community to add sections under each system instead of having an enormous table here. That way we can have more detailed and specific information on a per system basis, and here links to all the systems tested so far.
Home consoles
- Atari Jaguar
- Microsoft Xbox
- Microsoft Xbox 360
- NEC PC Engine
- Nintendo N64
- Nintendo NES / Famicom
- Nintendo Gamecube
- Nintendo Super NES / Super Famicom
- Nintendo Wii
- Sega Dreamcast
- Sega Genesis / MegaDrive
- Sega Master System
- Sega Saturn
- Sony Playstation
- Sony Playstation 2
Computers
Arcade Boards
- Capcom CPS-II
- Data East Caveman Ninja Hardware
- Irem M92
- Nintendo Playchoice 10
- Namco Gaplus
- Sega Model 2
- Seibu SPI
- SNK Hal 21
- SNK Neo Geo MVS
- Sony ZN-1
- Taito F2
- Taito FX-1B
- Taito F3
- Toaplan V1
- Toaplan V2
Remote control setup
In addition to the included remote control, it is possible to program OSSC to detect infrared signals from any remote which uses common NEC IR protocol. This is useful e.g. if one wants to minimize the number of remote controls in living room or if the included remote gets lost. Many TV remotes have optional control for DVD/VCR which may be used for controlling OSSC. Also, most AV receiver remotes allow controlling other devices (not only by the same manufacturer), so it's almost certainly possible to control OSSC with a suitable manufacturer code.
To configure OSSC for a new infrared RC, find a suitable manufacturer code (e.g. from Toshiba, NEC etc.) so that OSSC green LED blinks when remote buttons are pressed. Then cycle OSSC power on while holding BTN1. A target function name (e.g. "MENU") is displayed of the character LCD. Press the corresponding key on the remote control, after which you're prompted to confirm the new code if signal was detected correctly. Press the same key again to confirm, and then program rest of the functions. When done, new codes are effective immediately. Remember to save settings to make the new codes permanent.
Logitech Harmony
See this page for a tutorial on using the Logitech Harmony with the OSSC.
Philips Pronto
For IR codes and related files for Philips Pronto and compatible remotes, see this page.
Known issues / limitations
- interlaced content via VGA in RGBHV/RGBS mode works through a hack (TVP7002 issue).
- 240p signals using odd-field indicator like Chrono Cross or G Darius (arcade) work through a hack (TVP7002 issue). OSSC input must be pre-selected and not changed with such games.
- 320x240 and 256x240 optimized linetriple modes require phase adjusment each time the mode is initialized (TVP7002 issue - might be fixed with a workaround).
Firmware update
Firmware images. Since v0.74, a few firmware variants with following suffixes are available:
- -aud: Diy-audio (for those who have the add-on board installed)
- -jp: Japanese translation
- -aud_jp: Diy-audio + Japanese translation
FW update requires a microSD card (>2GB SDHC/SDXC cards supported from fw. 0.74 onwards) and a program to write the binary file as a disk image to the card (Win32 Disk Imager, dd etc.). The card can be then inserted to OSSC, after which the update process can be started by selecting the update option from the menu and following on-screen instructions. When update is complete, power should be turned off and SD card removed. New fw is activated when system is powered on next time. Settings are kept unless new menu options have been added.
See also - Video tutorial on updating the firmware using Windows.
Firmware update via JTAG
Firmware can also be updated via the JTAG connector and a suitable programmer such as the terasIC USB Blaster. A tutorial on how to do this is available here.
Firmware changelog and roadmap
v0.74
- New SD card controller supporting SDHC/SDXC cards
- Official fw image for boards with diy-audio
- Alternative fw images with menus translated into Japanese
v0.73
- Fixed adv. timing tweaker using previous values when updating parameters
- Added "Hsync tolerance" option to fix detection of certain Neo-Geo models
v0.72
- Some scanline rendering issues fixed
- Initial input option added
- Advanced timing tweaker - position, samplerate etc. adjusments
- R/G/B gain and offset control
- Sync filtering improvements
v0.71
- Interlace passthrough
- 480p/576p lineX2
- Alternating scanlines
v0.70
- YPbPr support for SCART and VGA
- Dedicated buttons for each input mode
- New menu structure
- Fix scanline idx and load of some settings
- Option to reset settings to defaults
- Extra remote shortcuts (scanline type, linemult mode)
- New options: ALC, Vsync threshold
- Automatic scanline mode (240p/288p)
- Reset line counters when changing input to avoid false mode detection
- Tweaked generic linetriple parameters for correct aspect ratio
v0.69
- Default fw on 1st batch of pre-assembled boards
Scheduled improvements
- Profiles (target: 0.7X)
- 240p/288p lineX4 and lineX5
Other feature requests
- Simple OSD
- Field offset adjustment for interlaced sources
- Overlay mask brightness control
- Scale2x/Super Eagle style graphics filters (requires new memory structure)
- De-dither filter for composite style faux transparencies (requires new memory structure)
- 480p -> 2x240p (duplicate every other line to bypass interpolation for e.g. GC GB player)
- 480i/576i lineX4 (960p/1152p)
- 240p passthrough
- Dedicated remote buttons for line2x, 3x and profiles
- Menu/backlight timeout
- Remote button for sampling phase adjustment