Difference between revisions of "OSSC Pro"
(→Expansion cards and adapters) |
(added link to Wobblings profile pack) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Ossc-logo-small.png]] | [[File:Ossc-logo-small.png]] | ||
| + | [[File:Ossc-Pro-front.jpg|600px|thumb|right|OSSC Pro front]] | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
* Full-range 24-bit RGB output through DVI/HDMI | * Full-range 24-bit RGB output through DVI/HDMI | ||
* Output from 240p to 2560x1440@60Hz (or to 2880x2160@60Hz with 2x pixel repetition) | * Output from 240p to 2560x1440@60Hz (or to 2880x2160@60Hz with 2x pixel repetition) | ||
| − | * | + | * Refresh rate multiplication support (up to 1080p120 or 720p240 output) |
* (HD-)CRT output modes including 1920x540 and 1080i | * (HD-)CRT output modes including 1920x540 and 1080i | ||
* Expansion card support with 36 GPIOs | * Expansion card support with 36 GPIOs | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
* Postprocessing options including masks and BFI | * Postprocessing options including masks and BFI | ||
* Character OLED display | * Character OLED display | ||
| − | * IR control using dedicated remote control, OSSC L336 remote or any other remote supporting | + | * IR control using dedicated remote control, OSSC L336 remote or any other remote supporting NEC IR protocol |
* Button & mini-joystick for basic control without remote | * Button & mini-joystick for basic control without remote | ||
* Micro-SD card socket for FW updates and additional profile storage | * Micro-SD card socket for FW updates and additional profile storage | ||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
|[[File:Ossc-logo-small.png|180px|link=]] | |[[File:Ossc-logo-small.png|180px|link=]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[https://github.com/marqs85/ossc_pro_hw/raw/master/doc/ossc_pro.xls List of components (v1. | + | |[https://github.com/marqs85/ossc_pro_hw/raw/master/doc/ossc_pro.xls List of components (v1.6)] |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 121: | Line 122: | ||
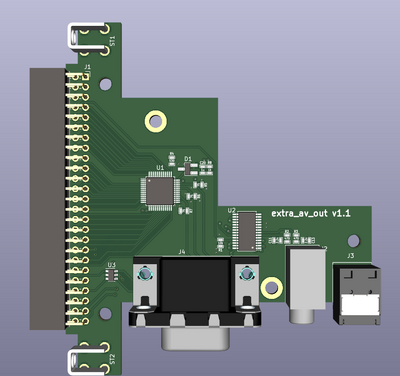
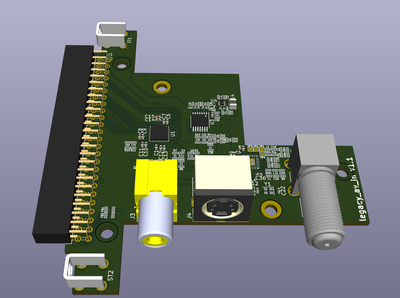
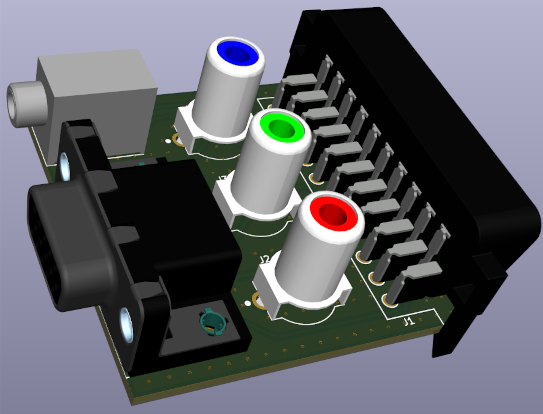
=== EXP (Legacy AV in expansion) === | === EXP (Legacy AV in expansion) === | ||
| − | The expansion card allows connecting S-video | + | The expansion card allows connecting S-video, composite video and RF sources to OSSC Pro. Audio is connected via AV 2xRCA connectors. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 131: | Line 132: | ||
| EXP_CVBS || 8 (tap twice) || Composite | | EXP_CVBS || 8 (tap twice) || Composite | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | EXP_RF || 8 (tap 3 times) || RF | + | | EXP_RF || 8 (tap 3 times) || RF |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 140: | Line 141: | ||
=== Additional AV inputs === | === Additional AV inputs === | ||
| − | See [[ | + | See [[#AV adapter]] and [[#Legacy AV input]] |
== Basic setup & usage == | == Basic setup & usage == | ||
| Line 250: | Line 251: | ||
| style="vertical-align:middle;" | Very fast | | style="vertical-align:middle;" | Very fast | ||
| style="vertical-align:middle;" | Fast | | style="vertical-align:middle;" | Fast | ||
| − | | style="vertical-align:middle;" | Instant | + | | style="vertical-align:middle;" | Instant* |
|- | |- | ||
| style="font-weight:bold;" | Transformations | | style="font-weight:bold;" | Transformations | ||
| Line 264: | Line 265: | ||
| style="vertical-align:middle;" | Scanlines, Masks, BFI | | style="vertical-align:middle;" | Scanlines, Masks, BFI | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | <nowiki>*</nowiki> guaranteed only when Scaling algo is not integer and Aspect is not Auto or 1:1 PAR | ||
=== Test pattern === | === Test pattern === | ||
| Line 273: | Line 275: | ||
=== Input select === | === Input select === | ||
| − | Selects the source, see [[ | + | Selects the source, see [[#AV inputs]] |
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== AV1-3 video in opt. === | === AV1-3 video in opt. === | ||
| Line 329: | Line 333: | ||
''ALV horizontal filter coefficient (duration for which ALC is applied after clamp).'' | ''ALV horizontal filter coefficient (duration for which ALC is applied after clamp).'' | ||
* '''16-128 pixels''': '''[default=16 pixels]''' | * '''16-128 pixels''': '''[default=16 pixels]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Lumacode ==== | ||
| + | ''Enables [https://github.com/c0pperdragon/LumaCode/wiki/Overview Lumacode] decoding for selected system. A Lumacode source is connected to Y RCA jack and uses AV2_RGsB logical input. You need to additionally select sampling preset for the target system, and possibly adjust phase and G/Y offset to get colors right.'' | ||
| + | * '''Off''': Lumacode decoding disabled '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''C64''': Lumacode decoding enabled for C64. | ||
| + | * '''Spectrum''': Lumacode decoding enabled for ZX Spectrum. | ||
| + | * '''Coleco / MSX''': Lumacode decoding enabled for Colecovision / MSX1. | ||
| + | * '''Intellivision''': Lumacode decoding enabled for Intellivision. | ||
| + | * '''NES''': Lumacode decoding enabled for NES. Use "SNES 256col" sampling preset. | ||
| + | * '''Atari GTIA''': Lumacode decoding enabled for Atari 8bit home computers. Use Line3x/4x/6x-320col mode with H. samplerate of 456. | ||
| + | * '''Atari VCS''': Lumacode decoding enabled for Atari 2600 (VCS). Use Line4x-320col mode with H. samplerate of 456. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Lumacode palette set ==== | ||
| + | ''Selects palette set for Lumacode modes'' | ||
| + | * '''PAL''': Palette matching PAL machines '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''Custom''': Select loaded custom palette set (see next option) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Custom Lumacode palette set ==== | ||
| + | ''Open menu for loading .txt file for custom palette set consisting of palettes for one or multiple supported sources. The file needs to be placed on lumacode/ subfolder on SD root. Click Expand on the right to view example config file containing all source entries.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | c64_pal | ||
| + | 000000,2a1b9d,7d202c,84258c,4c2e00,3c3c3c,646464,4fb3a5,7f410d,6351db,939393,bfd04a,339840,b44f5c,7ce587,ffffff | ||
| + | |||
| + | zx_pal | ||
| + | 000000,000000,0200FD,CF01CE,0100CE,CF0100,FF02FD,01CFCF,FF0201,00CF15,02FFFF,FFFF1D,00FF1C,CFCF15,CFCFCF,FFFFFF | ||
| + | |||
| + | msx_pal | ||
| + | 000000,5455ed,fc5554,ff7978,000000,d4524d,7d76fc,42ebf5,21b03b,21c842,ff7978,cccccc,c95bba,d4c154,e6ce80,ffffff | ||
| + | |||
| + | intv_pal | ||
| + | 0c0005,a7a8a8,fffcff,ff3e00,ffa600,faea27,00780f,00a720,6ccd30,002dff,5acbff,bd95ff,c81a7d,ff3276,3c5800,c9d464 | ||
| + | |||
| + | nes_pal | ||
| + | 000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,626262,001fb2,2404c8,5200b2,730076,800024,730b00,522800 | ||
| + | 244400,005700,005c00,005324,003c76,000000,ababab,0d57ff,4b30ff,8a13ff,bc08d6,d21269,c72e00,9d5400,607b00,209800 | ||
| + | 00a300,009942,007db4,000000,ffffff,53aeff,9085ff,d365ff,ff57ff,ff5dcf,ff7757,fa9e00,bdc700,7ae700,43f611,26ef7e | ||
| + | 2cd5f6,4e4e4e,ffffff,b6e1ff,ced1ff,e9c3ff,ffbcff,ffbdf4,ffc6c3,ffd59a,e9e681,cef481,b6fb9a,a9fac3,a9f0f4,b8b8b8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | tia_pal | ||
| + | 000000,404040,6C6C6C,909090,B0B0B0,C8C8C8,DCDCDC,ECECEC,444400,646410,848424,A0A034,B8B840,D0D050,E8E85C,FCFC68 | ||
| + | 702800,844414,985C28,AC783C,BC8C4C,CCA05C,DCB468,ECC878,841800,983418,AC5030,C06848,D0805C,E09470,ECA880,FCBC94 | ||
| + | 880000,9C2020,B03C3C,C05858,D07070,E08888,ECA0A0,FCB4B4,78005C,8C2074,A03C88,B0589C,C070B0,D084C0,DC9CD0,ECB0E0 | ||
| + | 480078,602090,783CA4,8C58B8,A070CC,B484DC,C49CEC,D4B0FC,140084,302098,4C3CAC,6858C0,7C70D0,9488E0,A8A0EC,BCB4FC | ||
| + | 000088,1C209C,3840B0,505CC0,6874D0,7C8CE0,90A4EC,A4B8FC,00187C,1C3890,3854A8,5070BC,6888CC,7C9CDC,90B4EC,A4C8FC | ||
| + | 002C5C,1C4C78,386890,5084AC,689CC0,7CB4D4,90CCE8,A4E0FC,003C2C,1C5C48,387C64,509C80,68B494,7CD0AC,90E4C0,A4FCD4 | ||
| + | 003C00,205C20,407C40,5C9C5C,74B474,8CD08C,A4E4A4,B8FCB8,143800,345C1C,507C38,6C9850,84B468,9CCC7C,B4E490,C8FCA4 | ||
| + | 2C3000,4C501C,687034,848C4C,9CA864,B4C078,CCD488,E0EC9C,442800,644818,846830,A08444,B89C58,D0B46C,E8CC7C,FCE08C | ||
| + | |||
| + | gtia_pal | ||
| + | 000000,111111,222222,333333,444444,555555,666666,777777,888888,999999,aaaaaa,bbbbbb,cccccc,dddddd,eeeeee,ffffff | ||
| + | 091900,192806,29370d,3a4714,4a561b,5a6522,6b7529,7b8430,8c9336,9ca33d,acb244,bdc14b,cdd152,dee059,eeef60,ffff67 | ||
| + | 300000,3d1108,4b2211,593319,674422,75552a,826633,90773b,9e8844,ac994c,baaa55,c7bb5d,d5cc66,e3dd6e,f1ee77,ffff80 | ||
| + | 4b0000,570f0c,631e18,6f2e24,7a3d30,874d3c,935c49,9f6b55,ab7b61,b68a6d,c39a79,cfa986,dbb892,e6c89e,f3d7aa,ffe7b7 | ||
| + | 550000,600e10,6b1c21,772a32,823843,8d4654,995465,a46276,af7187,bb7f98,c68da9,d19bba,dda9cb,e8b7dc,f3c5ed,ffd4fe | ||
| + | 4c0047,570d53,631b5f,6f286b,7b3678,874384,935190,9f5e9c,ab6ca9,b779b5,c387c1,cf94cd,dba2da,e7afe6,f3bdf2,ffcbff | ||
| + | 30007e,3b0b85,49198d,572796,65349f,7242a7,8050b0,8e5db8,9c6bc1,a979c9,b786d2,c594db,d3a2e3,e0afec,eebdf4,fccbfd | ||
| + | 0a0097,1a0e9d,2a1da4,3b2cab,4b3ab2,5b49b9,6c58c0,7c67c7,8c75ce,9c84d5,ad93dc,bda2e3,ceb0ea,debff1,eecef8,ffddff | ||
| + | 00008e,0c0d94,1b1e9c,2a2ea3,393eab,484eb2,575eba,666ec1,747ec9,838fd0,929fd8,a1afdf,b0bfe6,bfcfee,cedff5,ddeffd | ||
| + | 000e64,0c1e6e,192e78,263e83,324e8d,3f5e97,4c6ea2,587eac,658eb6,729ec1,7eaecb,8bbed5,98cee0,a4deea,b1eef4,beffff | ||
| + | 002422,09302e,153f3d,204d4c,2c5c5a,376a69,427978,4e8786,599695,65a4a4,70b3b2,7cc1c1,87d0d0,92dfde,9eeded,a9fcfc | ||
| + | 003200,0b3f0e,164d1c,225b2b,2d6839,397648,448456,509164,5b9f73,67ad81,72ba90,7ec89e,89d6ac,95e3bb,a0f1c9,acffd8 | ||
| + | 003400,0c410a,194f14,265c1e,336a28,407732,4c853c,599246,66a050,73ad5a,80bb64,8cc86e,99d678,a6e382,b3f18c,c0ff97 | ||
| + | 002a00,0f3807,1e460e,2d5416,3c621d,4b7124,5a7f2c,698d33,799b3b,88a942,97b849,a6c651,b5d458,c4e260,d3f067,e3ff6f | ||
| + | 0d1700,1d2606,2d350d,3d4514,4d541b,5d6422,6d7329,7d8330,8e9237,9ea23e,aeb145,bec14c,ced053,dee05a,eeef61,ffff68 | ||
| + | 330000,401008,4e2111,5b321a,694323,77542c,846535,92763e,9f8646,ad974f,bba858,c8b961,d6ca6a,e3db73,f1ec7c,fffd85 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== AV1-3 sync opt. === | === AV1-3 sync opt. === | ||
| Line 362: | Line 438: | ||
''Adjusts loop gain of H-PLL which affects sampling clock stability. A higher value makes the PLL react fast to changes in hsync interval which may make sampling more accurate but at the cost of increased jitter in output pixel clock. A small value ensures best compatibility, but sync jitter in the source (e.g. SNES) may result to sampling jitter on nearby scanlines. Increase for sources with sync jitter if your display is able to tolerate jitter in output clock.'' | ''Adjusts loop gain of H-PLL which affects sampling clock stability. A higher value makes the PLL react fast to changes in hsync interval which may make sampling more accurate but at the cost of increased jitter in output pixel clock. A small value ensures best compatibility, but sync jitter in the source (e.g. SNES) may result to sampling jitter on nearby scanlines. Increase for sources with sync jitter if your display is able to tolerate jitter in output clock.'' | ||
* '''0-3''': '''[default=0]''' | * '''0-3''': '''[default=0]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Ext. dotclk range ==== | ||
| + | ''Extended input dotclk range to enable exceeding ADC sampling rate spec.'' | ||
| + | * '''Off''': Disabled. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''On''': Setting required e.g. for 1920x1440_60 with reduced blanking. Might have adverse effects like slightly higher sampling jitter with other modes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== AV4 video in opt. === | === AV4 video in opt. === | ||
| Line 370: | Line 453: | ||
* '''Adaptive''': Full-range RGB. | * '''Adaptive''': Full-range RGB. | ||
| − | ==== Pixel | + | ==== Pixel decimation ==== |
| − | ''Enforces pixel | + | ''Enforces pixel decimation for sources with pixel repetition or multiplied horizontal resolution.'' |
| − | * '''Auto''': | + | * '''Auto''': Decimation follows metadata. '''[default]''' |
* '''1-10''': Manual override | * '''1-10''': Manual override | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== DV1 menu mode ==== | ||
| + | ''Enables dynamic reduction of pixel decimation factor when menu flag is set in metadata (Mister DV1 mode).'' | ||
| + | * '''Off''': Horizontal resolution is kept same regardless of menu flag. | ||
| + | * '''On''': Horizontal decimation is reduced when menu flag is set to improve overlay readability. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== EDID selection ==== | ||
| + | ''Selects EDID to AV4 port. New EDID is activated during boot or when AV4 input is activated.'' | ||
| + | * '''Default''': Default EDID indicating maximum supported AV capability of OSSC Pro.'''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''2ch audio''': EDID where HDMI LPCM audio support is limited to 2.0ch. Useful with sources like PS4 which assign audio channel count based on EDID and do not offer full customization. | ||
| + | * '''10bpc RGB+HDR''': EDID where 10bpc Deep Color and HDR support have been enabled. Useful for HDR bypass. Note: OSSC Pro converts signal to 8bpc and is only capable of flagging output as HLG, thus some loss of precision is likely to occur. | ||
| + | * '''720p max.''': EDID where indicated maximum resolution support is limited to 720p. Useful for LM downscaling (line drop) purposes. | ||
| + | * '''Custom''': Custom EDID loaded from SD card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Custom EDID load ==== | ||
| + | '' Opens a menu to load custom EDID file (edid/*.bin) from SD card. Up to 3 extension headers are support (i.e. max EDID size is 512 bytes).'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Line multiplier opt === | === Line multiplier opt === | ||
| Line 425: | Line 526: | ||
===== Reset preset ===== | ===== Reset preset ===== | ||
''Resets parameters of selected preset to default values.'' | ''Resets parameters of selected preset to default values.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Scaler opt. === | === Scaler opt. === | ||
| Line 434: | Line 537: | ||
* '''720x576 (50Hz)''': Standard 576p output supported by most HDTVs. | * '''720x576 (50Hz)''': Standard 576p output supported by most HDTVs. | ||
* '''720x576 WS (50Hz)''': Standard widescreen 576p output supported by most HDTVs. | * '''720x576 WS (50Hz)''': Standard widescreen 576p output supported by most HDTVs. | ||
| − | * '''1280x720 ( | + | * '''1280x720 (24-240Hz)''': Standard 720p output supported by majority of HDTVs. |
| − | * '''1280x1024 ( | + | * '''1280x1024 (24-150Hz)''': SXGA mode for 5:4 desktop monitors. |
| − | * '''1920x1080i ( | + | * '''1920x1080i (48-120Hz)''': Standard 1080i output supported by most modern HDTVs. |
| − | * '''1920x1080 ( | + | * '''1920x1080 (24-120Hz)''': Standard 1080p output supported by all modern HDTVs. '''[default]''' |
| − | * '''1600x1200 ( | + | * '''1600x1200 (24-100Hz)''': UXGA mode for 4:3 desktop monitors. |
| − | * '''1920x1200 ( | + | * '''1920x1200 (24-100Hz)''': WUXGA mode for 16:10 desktop monitors. Uses CVT timings (RB for 60Hz). |
| − | * '''1920x1440 ( | + | * '''1920x1440 (24-90Hz)''': 4:3 1440p mode for compatible displays. Uses CVT timings (RB for 60Hz). |
| − | * '''2560x1440 ( | + | * '''2560x1440 (24-72Hz)''': 16:9 1440p mode for compatible displays. Uses CVT-RB timings. |
| − | * '''2880x2160 ( | + | * '''2880x2160 (24-60Hz)''': 4:3 2160p mode for compatible displays. Uses CVT-RB timings and 2x pixel repetition. |
==== CRT output mode ==== | ==== CRT output mode ==== | ||
''Selects output mode for CRT. Modes are meant for video DACs, not HDMI devices. Supported output refresh range is shown in braces.'' | ''Selects output mode for CRT. Modes are meant for video DACs, not HDMI devices. Supported output refresh range is shown in braces.'' | ||
| − | * '''240p ( | + | * '''240p (24-240Hz)''': Non-interlaced 60Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. '''[default]''' |
| − | * '''240p WS ( | + | * '''240p WS (24-240Hz)''': Non-interlaced 60Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''288p ( | + | * '''288p (24-250Hz)''': Non-interlaced 50Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''288p WS ( | + | * '''288p WS (24-250Hz)''': Non-interlaced 50Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''480i ( | + | * '''480i (48-180Hz)''': Interlaced 60Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''480i WS ( | + | * '''480i WS (48-180Hz)''': Interlaced 60Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''576i ( | + | * '''576i (48-150Hz)''': Interlaced 50Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''576i WS ( | + | * '''576i WS (48-150Hz)''': Interlaced 50Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''480p ( | + | * '''480p (24-170Hz)''': 480-line mode for 31kHz capable CRT monitors. |
| − | * '''540p ( | + | * '''540p (24-180Hz)''': 540-line mode for 1080i capable HD-CRT TVs. |
| − | * '''1024x768 ( | + | * '''1024x768 (24-240Hz)''': XGA mode for CRT monitors. |
| − | * '''1280x960 ( | + | * '''1280x960 (24-160Hz)''': QuadVGA mode for CRT monitors. |
| + | * '''2048x1536 (24-60Hz)''': QuadXGA mode for CRT monitors or tablet displays. | ||
==== Output type ==== | ==== Output type ==== | ||
| Line 467: | Line 571: | ||
''Defines output refresh rate and how it is generated.'' | ''Defines output refresh rate and how it is generated.'' | ||
* '''On''': Output refresh rate is locked to input. Minimizes latency, but any interruption in input (e.g. video mode change) may temporarily break sync on output side. '''[default]''' | * '''On''': Output refresh rate is locked to input. Minimizes latency, but any interruption in input (e.g. video mode change) may temporarily break sync on output side. '''[default]''' | ||
| − | |||
* '''Off (source Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not directly generated from input, but using an external clock source instead. Refresh rate is set to match input as closely as possible. | * '''Off (source Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not directly generated from input, but using an external clock source instead. Refresh rate is set to match input as closely as possible. | ||
| + | * '''Off (preset Hz)''': Output refresh rate is taken from the output preset, see [[#Adv. disp timing]] | ||
* '''Off (50Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 50Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | * '''Off (50Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 50Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | ||
* '''Off (60Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 60Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | * '''Off (60Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 60Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | ||
* '''Off (100Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 100Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | * '''Off (100Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 100Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | ||
* '''Off (120Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 120Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | * '''Off (120Hz)''': Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 120Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Framelock multiplier ==== | ||
| + | ''Enables refresh rate multiplication in framelocked mode.'' | ||
| + | * '''1-10x''': Refresh rate multiplier. Be aware of above output rate limits as exceeding it results to falling back into highest refresh preset without framelock.'''[default=1x]''' | ||
==== Aspect ratio ==== | ==== Aspect ratio ==== | ||
| Line 493: | Line 601: | ||
* '''Lanczos3&3_sharp''': Sharpened version only applied for edges. | * '''Lanczos3&3_sharp''': Sharpened version only applied for edges. | ||
* '''Lanczos4''': Similar to Lanczos3 but with reduced smoothening. | * '''Lanczos4''': Similar to Lanczos3 but with reduced smoothening. | ||
| − | * '''GS sharp''': General scaling with | + | * '''GS sharp''': General scaling with sharp interpolation. |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''GS medium''': General scaling with medium-sharp interpolation. |
| − | * '''Custom | + | * '''GS soft''': General scaling with soft interpolation. |
| + | * '''Custom''': Select loaded custom configuration (see next option) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Custom SCL alg ==== | ||
| + | '' Opens a menu to load custom scaler algorithm configuration file (scl_alg/*.cfg) from SD card. A configuration file consists of 2 or 4 lines in the format below. 2 first lines define scaling algorithm for X/Y direction. 2 extra lines can be optionally added to enable edge-adaptive mode and set X/Y scaling algorithm for edge content. Each line either names a preset algorithm (nearest, lanczos3, lanczos3_13, lanczos4, gs_sharp, gs_medium, gs_soft) or defines a filename for custom coefficient .txt file placed on the same folder. Custom coefficients must be in Mister [https://github.com/MiSTer-devel/Filters_MiSTer/ format] and define 64 phases (both 9bit & 10bit coeffs are supported). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | X | ||
| + | Y | ||
| + | (edge: X) | ||
| + | (edge: Y) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
==== Edge threshold ==== | ==== Edge threshold ==== | ||
| Line 534: | Line 653: | ||
==== Adv. timing ==== | ==== Adv. timing ==== | ||
''Refer to [[#A-LM Adv. timing]].'' | ''Refer to [[#A-LM Adv. timing]].'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Output opt. === | === Output opt. === | ||
| Line 562: | Line 683: | ||
* '''Off''': No VRR metadata sent. '''[default]''' | * '''Off''': No VRR metadata sent. '''[default]''' | ||
* '''Freesync''': Freesync infoframe sent. | * '''Freesync''': Freesync infoframe sent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== HDMI combined sync ==== | ||
| + | ''Enables RGBS output from HDMI port when using HDMI to VGA DACs.'' | ||
| + | * '''Off''': Standard HV sync output. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''On''': Combined sync output. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== CSync combiner ==== | ||
| + | ''Selects sync combiner type for HDMI and Extra AV output csync output.'' | ||
| + | * '''Type A (AND)''': H+V sync are combined with AND logic. Falling hsync edges in consistent position except during VSYNC when not present. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''Legacy (XNOR)''': Falling hsync edges present also during VSYNC but with some offset in position. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Full TX setup ==== | ||
| + | ''Sets whether TX initialization is done every time a video mode changes.'' | ||
| + | * '''Off''': TX is kept on during mode changes. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''On''': TX is reinitialized when input/output mode changes, resulting to a short blank. Needed if display permanently loses picture / audio upon video mode changes. | ||
==== 1080p120 preset ==== | ==== 1080p120 preset ==== | ||
| Line 577: | Line 713: | ||
==== Adv. disp timing ==== | ==== Adv. disp timing ==== | ||
''Allows changing output preset parameters. Useful mainly for users of CRTs (overscan mitigation) and HD-Ready LCDs/PDPs with native resolutions not covered by existing presets. Can be also used to test display refresh rate limits in test pattern mode, or set custom refresh rate for SCL Framelock off (preset Hz) mode.'' | ''Allows changing output preset parameters. Useful mainly for users of CRTs (overscan mitigation) and HD-Ready LCDs/PDPs with native resolutions not covered by existing presets. Can be also used to test display refresh rate limits in test pattern mode, or set custom refresh rate for SCL Framelock off (preset Hz) mode.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Reset disp preset ==== | ||
| + | ''Resets parameters for currently active (or one selected under "Adv. disp timing") preset.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Audio opt. === | === Audio opt. === | ||
| Line 622: | Line 763: | ||
* '''SPDIF''': Digital toslink audio input. | * '''SPDIF''': Digital toslink audio input. | ||
* '''AV4 (digital)''': Digital HDMI audio. '''[default]''' | * '''AV4 (digital)''': Digital HDMI audio. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== EXP audio source ==== | ||
| + | ''Selects audio source for Legacy AV Input expansion.'' | ||
| + | * '''AV2 (analog)''': AV2 audio (2x RCA jacks). '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''AV3 (analog)''': AV3 audio (3.5mm jack). | ||
| + | * '''SPDIF''': Digital toslink audio input. | ||
==== 3.5mm jack assign ==== | ==== 3.5mm jack assign ==== | ||
| Line 627: | Line 774: | ||
* '''AV3 input''': The jack functions as audio input for AV3. '''[default]''' | * '''AV3 input''': The jack functions as audio input for AV3. '''[default]''' | ||
* '''AV1 output''': Audio from SCART input is routed to the jack, e.g. enabling analog passthru to AVR. | * '''AV1 output''': Audio from SCART input is routed to the jack, e.g. enabling analog passthru to AVR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Scanline opt. === | === Scanline opt. === | ||
| Line 676: | Line 825: | ||
===== Sub-column N str ===== | ===== Sub-column N str ===== | ||
''Strength for Nth sub-column, 0% disables column overlay.'' | ''Strength for Nth sub-column, 0% disables column overlay.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Post-proc. === | === Post-proc. === | ||
| Line 698: | Line 849: | ||
* '''JVC''': Mask imitating generic JVC monitor. | * '''JVC''': Mask imitating generic JVC monitor. | ||
* '''VGA''': Mask imitating generic VGA monitor. | * '''VGA''': Mask imitating generic VGA monitor. | ||
| − | * '''Custom | + | * '''Custom''': Select loaded custom shadow mask (see next option) |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==== Custom shadow mask ==== | ||
| + | '' Opens a menu to load custom shadow mask file (shmask/*.txt) from SD card. The file must be in Mister [https://github.com/MiSTer-devel/ShadowMasks_MiSTer/ format]. | ||
| − | ==== BFI for | + | ==== Sh. mask strength ==== |
| − | ''Enables black frame insertion feature for modes | + | * '''6-100%''': Strength of the selected shadow mask'''[default=100%]''' |
| − | * ''' | + | |
| + | ==== BFI for duplicated frames ==== | ||
| + | ''Enables black frame insertion feature for modes with framelock multiplier >1x. Reducing image persistence can be used to improve motion resolution at the cost of some flicker.'' | ||
| + | * '''After N src frames''': BFI is enabled for remaining duplicates after showing original frame N times. | ||
* '''Off''': BFI disabled. '''[default]''' | * '''Off''': BFI disabled. '''[default]''' | ||
==== BFI strength ==== | ==== BFI strength ==== | ||
| − | ''Sets the strength of BFI to trade off motion resolution for improved brightness / reduced flicker'' | + | ''Sets the strength of BFI for frames its applied to. Can be used to trade off motion resolution for improved brightness / reduced flicker'' |
* '''6-100%''': Sets opaqueness of the black mask applied over a duplicated frame. '''[default=100%]''' | * '''6-100%''': Sets opaqueness of the black mask applied over a duplicated frame. '''[default=100%]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Expansion opt. === | === Expansion opt. === | ||
| Line 730: | Line 888: | ||
==== Legacy AV opt. ==== | ==== Legacy AV opt. ==== | ||
''Sets various options for this expansion card'' | ''Sets various options for this expansion card'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Signal information === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Displays information about input & output timings, firmware and uptime.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== Settings === | === Settings === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Power-up state ==== | ||
| + | ''Selects the operational state which is activated when power supply is connected.'' | ||
| + | * '''Standby''': Unit is placed in standby mode. '''[default]''' | ||
| + | * '''Active''': Unit is placed in active mode. | ||
==== Initial input ==== | ==== Initial input ==== | ||
| Line 748: | Line 919: | ||
* '''10s''': status shown for 10 seconds. | * '''10s''': status shown for 10 seconds. | ||
* '''Off''': Status is not displayed. | * '''Off''': Status is not displayed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== OSD cursor color ==== | ||
| + | ''Sets highlight color for OSD'' | ||
| + | * '''Green|Cyan|Red|Magenta|Yellow''': Highlight color. '''[default=Yellow]''' | ||
==== Fan PWM ==== | ==== Fan PWM ==== | ||
| Line 760: | Line 935: | ||
''Learns keycodes from an IR remote. Press prompted function key on a new remote and confirm it by pressing the key again. Once all functions have been configured, new keymap settings are saved. Notes:'' | ''Learns keycodes from an IR remote. Press prompted function key on a new remote and confirm it by pressing the key again. Once all functions have been configured, new keymap settings are saved. Notes:'' | ||
* Any unused functions can be bound to a single unused key | * Any unused functions can be bound to a single unused key | ||
| − | * If you entered a wrong key, press PCB button to go back to setup of previous function. | + | * If you entered a wrong key, press PCB button to go back to setup of previous function. |
| + | |||
| + | * To clear custom bindings and reset to default - Choose the "Bind IR remote" option and then immediately press the PCB button (the circle shaped button) on the front of the OSSC. This will cancel setup of the new remote and prompt if ther default keymap should be loaded. Press the navigation control on the front of the OSSC Pro to the right to confirm and reset to default. | ||
==== Load profile ==== | ==== Load profile ==== | ||
| Line 766: | Line 943: | ||
==== Save profile ==== | ==== Save profile ==== | ||
| − | ''Saves profile into selected slot in on-board flash. Settings (i.e. contents of settings menu which are not part of a profile) are saved simultaneously. Profile name to be written can be overridden by prof_n_i.txt on SD card root (one line per profile, max. | + | ''Saves profile into selected slot in on-board flash. Settings (i.e. contents of settings menu which are not part of a profile) are saved simultaneously. Profile name to be written can be overridden by prof_n_i.txt on SD card root (one line per profile, max. 17 chars per name, see "How to rename profiles" below for more information).'' |
==== SD Load profile ==== | ==== SD Load profile ==== | ||
| Line 772: | Line 949: | ||
==== SD Save profile ==== | ==== SD Save profile ==== | ||
| − | ''Saves profile into selected slot on SD card. Settings (i.e. contents of settings menu which are not part of a profile) are saved simultaneously to SD card on a separate file. Profile name to be written can be overridden by prof_n.txt on SD card root (one line per profile, max. | + | ''Saves profile into selected slot on SD card. Settings (i.e. contents of settings menu which are not part of a profile) are saved simultaneously to SD card on a separate file. Profile name to be written can be overridden by prof_n.txt on SD card root (one line per profile, max. 17 chars per name, see "How to rename profiles" below for more information ).'' |
==== Reset profile ==== | ==== Reset profile ==== | ||
| Line 780: | Line 957: | ||
''Firmware update function. New version is displayed on the screen after which update can be initiated by pressing "->" via remote or PCB joystick. Below are descriptions for error codes which may prevent the upgrade process.'' | ''Firmware update function. New version is displayed on the screen after which update can be initiated by pressing "->" via remote or PCB joystick. Below are descriptions for error codes which may prevent the upgrade process.'' | ||
* Error -1: SD card not detected. | * Error -1: SD card not detected. | ||
| − | * Error -2: FW file not found. Rename the file as ossc_pro.bin and ensure it's on the root of the SD card. | + | * Error -2: FW file not found. Rename the file as ossc_pro.bin and ensure it's on the root of the SD card. If active firmware is v0.75 or below, make also sure SD card is formatted as FAT32. |
* Error -3...-5: FW header error. The firmware file is corrupted. | * Error -3...-5: FW header error. The firmware file is corrupted. | ||
* Error -6: Target offset not aligned to flash sector. Firmware file contains invalid offset. | * Error -6: Target offset not aligned to flash sector. Firmware file contains invalid offset. | ||
| Line 786: | Line 963: | ||
* Error -8: FW data read error. Error while copying the firmware file to DRAM. | * Error -8: FW data read error. Error while copying the firmware file to DRAM. | ||
* Error -9: CRC error while checking the data copied to DRAM. Change to test pattern or restart the device, and try again. | * Error -9: CRC error while checking the data copied to DRAM. Change to test pattern or restart the device, and try again. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
=== How to rename profiles === | === How to rename profiles === | ||
| Line 795: | Line 974: | ||
Remember that Windows can hide file extensions from the user when using file explorer and the default settings. Ensure the file is called "prof_n_i.txt" and not "prof_n_i" or even "prof_n_i.txt.txt" | Remember that Windows can hide file extensions from the user when using file explorer and the default settings. Ensure the file is called "prof_n_i.txt" and not "prof_n_i" or even "prof_n_i.txt.txt" | ||
| − | 2) Edit this file so that each line is the name of the profile. Terminate the line with a return. You can use a maximum of | + | 2) Edit this file so that each line is the name of the profile. Terminate the line with a return. You can use a maximum of 17 characters per name |
3) Ensure your edited file is saved to the to SD card. Safely remove the SD card from your computer and re-insert it into the OSSC Pro | 3) Ensure your edited file is saved to the to SD card. Safely remove the SD card from your computer and re-insert it into the OSSC Pro | ||
| Line 827: | Line 1,006: | ||
=== Computers === | === Computers === | ||
| − | * | + | * [[Atari 8-bit family]] |
| − | * | + | * [[Atari ST]] |
| − | * DOS PC | + | * [[Amiga|Commodore Amiga]] |
| − | * MSX | + | * [[C64|Commodore 64]] |
| − | * PC-9801 | + | * [[DOS PC]] |
| − | * | + | * [[MSX]] |
| + | * [[PC-9801]] | ||
| + | * [[X68000|Sharp X68000]] | ||
=== Arcade Boards === | === Arcade Boards === | ||
| Line 843: | Line 1,024: | ||
* Taito [[FX-1B]] | * Taito [[FX-1B]] | ||
* '''Toaplan [[V2]]''' | * '''Toaplan [[V2]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Basic downscaling for modern computers/consoles === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The OSSC Pro is popular amongst classic CRT display users as a downscaler. Emulated games or modern pixel art titles can often be downscaled to a classic CRT display. How effective this process is depends on the base resolution of the game. For instance a game with 240p base resolution running at 720p on a console can take advantage of the OSSC Pros 3x line drop mode to be downscaled perfectly (since 240 x 3 = 720). The wiki page [[Scaling_pixel_art_tiles_on_modern_consoles/computers_with_Morph_4K|here]] lists a number of titles and their base resolutions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | While the unit has several output options to suit classic displays, for pixel perfect results the following modes can be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 480p to 240p (2x line drop or scaler) - Equivalent to /2 prescale on the Morph for any title running at 480p. | ||
| + | * 720p to 240p (3x line drop or scaler) – Equivalent to /3 prescale on the Morph for any title running at 720p. | ||
| + | * 1080p to 240p (5x line drop or scaler) - Equivalent to /5 prescale on the Morph for any title running at 1080p. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Games that do not adhere to these specs (for instance the game Pocky and Rocky Re-shrined which has a 480x2270 base resolution and requires a /4 pre-scale at 1080p) can still be downscaled, but may not look good. For instance pixel heights may not be uniform or parts of the image may appear squashed, distorted or missing entirely. In these instances, use of 480i output mode may be preferable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remember that many modern pixel art titles run in widescreen. If your CRT is 4:3 aspect ratio and does not have aspect ratio correction, you will need to use scaler mode in order to convert the aspect ratio appropriately. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Wobbling Pixels Optimal Profiles == | ||
| + | |||
| + | An optional package of pre-made profiles for the OSSC Pro has been created by user Wobbling Pixels. This package can be downloaded [https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1sIzua0dNnj3SIoiKp696zglKSZnKVpcIQSq6_7U3wQg/edit?gid=1693314832#gid=1693314832 here] and placed onto your SD card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The profiles are designed for use when upscaling retro consoles, rather than downscaling or using a CRT. They are designed to get the sharpest possible image from the source material. Full instructions are provided in the link above. | ||
== Expansion cards and adapters == | == Expansion cards and adapters == | ||
| Line 898: | Line 1,099: | ||
[[File:legacy_av_in.png|400px]] | [[File:legacy_av_in.png|400px]] | ||
| − | Legacy AV input card adds support for composite, S-video. RF support is | + | Legacy AV input card adds support for composite, S-video and RF. RF support is work in progress and is not guaranteed to produce clean video with all sources. Supported video formats include PAL, PAL60, NTSC and NTSC50 (?). |
| − | Audio from composite and s-video sources need to be connected to AV2 RCA inputs as cost of the board is kept at minimum. The video is digitized with a dedicated cvbs/s-video decoder chip which has more limited configurability with regards to sync processing and sampling (e.g. no optimal timings supported). A dedicated list of processing options related to cvbs/s-video decoding is found under Expansion opt -> Legacy AV opt. | + | Audio from composite and s-video sources need to be connected to AV2 RCA inputs as cost of the board is kept at minimum. The video is digitized with a dedicated cvbs/s-video decoder chip which has more limited configurability with regards to sync processing and sampling (e.g. no optimal timings supported). A dedicated list of processing options related to cvbs/s-video/rf decoding is found under Expansion opt -> Legacy AV opt. |
| + | |||
| + | To scan for RF source, launch "RF chscan (2min)" with correct TV standard from the menu. Wait until the scan has finished (which happens if a channel is found or end of the range is reached). The RF input can be now selected. The channel tuning settings are included when a profile is saved/loaded. | ||
=== AV adapter === | === AV adapter === | ||
| Line 923: | Line 1,126: | ||
== Firmware update == | == Firmware update == | ||
| − | Firmware is updated via microSD card. Download .bin file for the latest release from [https://github.com/marqs85/ossc_pro/releases github] | + | Firmware is updated via microSD card. Download .bin file for the latest release from [https://github.com/marqs85/ossc_pro/releases github] and: |
| + | |||
| + | '''Option 1)''' Rename it as ossc_pro.bin and place it to root of FAT32-formatted SD card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Option 2)''' (Supported if running fw >= 0.78) Place it into "fw" folder on FAT32 or exFAT formatted SD card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Launch upgrade via Settings menu. The device enters standby mode when update is finished. If you get an error code during update, refer [[#Fw. update|here]] | ||
=== Firmware update via JTAG === | === Firmware update via JTAG === | ||
| Line 931: | Line 1,140: | ||
== Firmware changelog and roadmap == | == Firmware changelog and roadmap == | ||
| − | === v0.75 === | + | === v0.81 === |
| + | * Robustness fixes | ||
| + | ** SD card corruption and freezing issues resolved | ||
| + | ** Csync output AND-type implementation added as default | ||
| + | ** ADV7280 comb filter config setting corrected | ||
| + | * Support for custom Lumacode palettes added | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Older versions === | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== v0.80 ==== | ||
| + | * 384p and 768i CRT output presets added | ||
| + | * Legacy AV options expanded | ||
| + | * minor fixes related to audio metadata refresh and picture position adjustment | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== v0.79 ==== | ||
| + | * support for 24Hz HDMI sources added | ||
| + | * support for higher framelock/BFI multipliers added | ||
| + | * “720p max” EDID preset added | ||
| + | * Full TX setup compatibility option added | ||
| + | * various robustness and timing improvements | ||
| + | * Lumacode support for Atari GTIA and Atari VCS added | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== v0.78 ==== | ||
| + | * 1920x1440@60 input support added for both analog and digital sources | ||
| + | * 1152x864_75 sampling preset added | ||
| + | * 2048x1536 and 2560x1920 (PR2x) output presets added | ||
| + | * LG VRR compatibility fixed | ||
| + | * Workaround for Mister SNES core jitter added | ||
| + | * Scaler framelocking consistency improved | ||
| + | * Support for RF added (legacy AV expansion) | ||
| + | * UI improvements | ||
| + | ** infoscreen display when OSD is off | ||
| + | ** OSD highlight color option | ||
| + | ** Profile number entry via remote | ||
| + | ** FW file selection menu | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== v0.77 ==== | ||
| + | * new features added for HDMI frontend | ||
| + | ** EDID presets and custom EDID option | ||
| + | ** pixel decimation by FPGA (previously RX de-repetition) | ||
| + | * new features added for SDP frontend | ||
| + | ** audio source selection | ||
| + | ** CTI options | ||
| + | * 1080p line drop modes added | ||
| + | * signal info display option added into menu | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== v0.76 ==== | ||
| + | * Lumacode support added | ||
| + | * New line drop modes added | ||
| + | * Custom scl_alg/shmask loading improved | ||
| + | * Shadow mask strength adjustment option added | ||
| + | * 10bit coefficient support added for scaling algorithms | ||
| + | * Power-up state option added | ||
| + | * Added support for exFAT | ||
| + | * Fixed number of minor bugs | ||
| + | ** SPDIF output active when power off | ||
| + | ** random bobbing with analog HV sync sources when sync edges are closely aligned | ||
| + | ** Garbage on topmost line with LM Bob deinterlace | ||
| + | ** 0x00/0xff extreme RGB values clamped with HDMI input | ||
| + | ** scanline issues on 2160p mode | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== v0.75 ==== | ||
* added support for Legacy AV in expansion | * added support for Legacy AV in expansion | ||
* added support for YPbPr output via extra_av_out expansion | * added support for YPbPr output via extra_av_out expansion | ||
| Line 939: | Line 1,210: | ||
* improved audio output compatibility | * improved audio output compatibility | ||
* various small bug fixes | * various small bug fixes | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== v0.74 ==== | ==== v0.74 ==== | ||
Latest revision as of 06:30, 31 January 2026
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 AV inputs
- 3 Basic setup & usage
- 4 Settings
- 4.1 Input select
- 4.2 AV1-3 video in opt.
- 4.2.1 Video LPF
- 4.2.2 Reverse LPF
- 4.2.3 YPbPr input Color Space
- 4.2.4 R/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb offset
- 4.2.5 R/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb gain
- 4.2.6 Clamp strength
- 4.2.7 Clamp/ALC position
- 4.2.8 Clamp width
- 4.2.9 Clamp/ALC on coast
- 4.2.10 Auto level ctl (ALC)
- 4.2.11 ALC V filter
- 4.2.12 ALC H filter
- 4.2.13 Lumacode
- 4.2.14 Lumacode palette set
- 4.2.15 Custom Lumacode palette set
- 4.3 AV1-3 sync opt.
- 4.4 AV4 video in opt.
- 4.5 Line multiplier opt
- 4.6 Scaler opt.
- 4.6.1 DFP output mode
- 4.6.2 CRT output mode
- 4.6.3 Output type
- 4.6.4 Framelock
- 4.6.5 Framelock multiplier
- 4.6.6 Aspect ratio
- 4.6.7 Scaling algorithm
- 4.6.8 Custom SCL alg
- 4.6.9 Edge threshold
- 4.6.10 Deinterlace mode
- 4.6.11 Motion shift
- 4.6.12 Generic samplerate
- 4.6.13 240p/288p mode
- 4.6.14 350-400p mode
- 4.6.15 480i/576i mode
- 4.6.16 480-512p mode
- 4.6.17 576p mode
- 4.6.18 Adv. timing
- 4.7 Output opt.
- 4.8 Audio opt.
- 4.9 Scanline opt.
- 4.10 Post-proc.
- 4.11 Expansion opt.
- 4.12 Signal information
- 4.13 Settings
- 4.14 How to rename profiles
- 5 Compatibility and special configuration
- 6 Wobbling Pixels Optimal Profiles
- 7 Expansion cards and adapters
- 8 Firmware update
- 9 Firmware changelog and roadmap
- 10 Info for developers
Introduction
OSSC Pro is an advanced low-latency video digitizer, scan converter and scaler designed primarily for connecting retro video game consoles and home computers to modern displays.
If you're new to the OSSC and scalers/processors in general, you may wish to jump to the quick start guide.
Features
- Detection and digitization of various analog SDTV/EDTV/HDTV/PC modes
- Up to ~165MHz sampling clock for both analog and digital video sources, supporting high resolutions like 1080p@60
- Various sampling presets for classic consoles and home computers
- Ultra low latency line multiplication for 240p, 480i, 288p, 576i, 384p, 480p, 576p and 720p sources
- Full-fledged scaler mode with configurable polyphase scaling filter
- Framelocked and free-running scaler modes to select between judder-free or interrupt-free operation
- Deinterlacer supporting motion adaptive, weave and bob algorithms for 480i, 576i, 960i, and 1080i
- All video processing done in RGB domain (8bpc) - no internal conversion to subsampled YCbCr
- Video and sync LPF for less-than optimal input signals
- Various AV input options, both analog and digital (see table below)
- Full-range 24-bit RGB output through DVI/HDMI
- Output from 240p to 2560x1440@60Hz (or to 2880x2160@60Hz with 2x pixel repetition)
- Refresh rate multiplication support (up to 1080p120 or 720p240 output)
- (HD-)CRT output modes including 1920x540 and 1080i
- Expansion card support with 36 GPIOs
- Emulated scanlines with fully configurable strength and interval
- Postprocessing options including masks and BFI
- Character OLED display
- IR control using dedicated remote control, OSSC L336 remote or any other remote supporting NEC IR protocol
- Button & mini-joystick for basic control without remote
- Micro-SD card socket for FW updates and additional profile storage
- USB port (FS) for future expandability
Board versions and availability
Production board
Pre-assembled boards are sold worldwide by:
| VideoGamePerfection.com |
|---|
| List of components (v1.6) |
More information & discussion
AV inputs
Input is selected via remote key / OSD input menu. The table below summarizes available inputs and their corresponding remote hotkeys.
AV1 (SCART)
The SCART connector of OSSC Pro supports a number of video/sync formats. SCART-RGB sources can be connected as-is while other formats require passthru cables/adapters.
| Input name | Remote hotkey | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AV1_RGBS | 1 | For video level c-sync only. Sync can be also extracted from composite video / luma. |
| AV1_RGsB | 4 | Use suitable adapter / SCART cable. |
| AV1_YPbPr | 4 (tap twice) | Use YPbPr to SCART passthru adapter. Some suitable adapters are sold online (e.g. this) but most don't include audio jacks. |
| AV1_RGBHV | 7 | Needs a custom adapter/cable which routes HSYNC to SCART pin 12 and VSYNC to pin 10. |
| AV1_RGBCS | 7 (tap twice) | For TTL c-sync only. Needs a custom adapter/cable which routes CSYNC to SCART pin 12. |
AV2 (5xRCA)
The 5xRCA connector set of OSSC Pro supports RGsB or YPbPr sources.
| Input name | Remote hotkey | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AV2_YPbPr | 2 | Use YPbPr to SCART passthru adapter. Some suitable adapters are sold online (e.g. this) but most don't include audio jacks. |
| AV2_RGsB | 2 (tap twice) | Use suitable adapter / SCART cable. |
AV3 (HD-15 "VGA" + 3.5mm jack)
The HD-15 connector allows connecting e.g. a classic PC or Dreamcast to OSSC Pro.
| Input name | Remote hotkey | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AV3_RGBHV | 3 | Normal VGA pinout |
| AV3_RGBCS | 3 (tap twice) | For TTL c-sync only (connected to hsync pin) |
| AV3_RGBS | 6 | For video level c-sync only. Sync is connected to HD-15 pin 4 via a custom adapter / cable. |
| AV3_RGsB | 9 | Use suitable adapter / cable. |
| AV3_YPbPr | 9 (tap twice) | Use suitable adapter / cable. |
AV4 (HDMI)
The HDMI connector allows connecting digital AV sources to OSSC Pro. HDCP is not supported.
| Input name | Remote hotkey | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AV4 | 5 |
EXP (Legacy AV in expansion)
The expansion card allows connecting S-video, composite video and RF sources to OSSC Pro. Audio is connected via AV 2xRCA connectors.
| Input name | Remote hotkey | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| EXP_Svideo | 8 | S-video |
| EXP_CVBS | 8 (tap twice) | Composite |
| EXP_RF | 8 (tap 3 times) | RF |
Toslink
The toslink input supports LPCM 44.1/48/96kHz and compressed bitstream (Dolby Digital, DTS) formats. Toslink input can be mapped to any of the above AV inputs. The audio stream is forwarded as-is to HDMI transmitter.
Additional AV inputs
See #AV adapter and #Legacy AV input
Basic setup & usage
Connectivity
Connect your AV sources and display to OSSC Pro.
Power
OSSC requires an external DC power supply. A unit that outputs 5 volts DC with at least 2 Amp (with any expansion cards and/or HDMI adapters 2.5A is highly recommended). The tip must be 2.1 x 5.5mm and centre positive.
Do not use a power supply rated for AC output, or a power supply rated higher than 5 volts DC. An overvoltage protection (5.5V threshold) is present but extensive misuse can damage the board.
After connecting power, OSSC Pro enters standby mode which is indicated by red LED.
Remote control
OSSC Pro operates with a dedicated infrared remote. Key functionality is listed below.
- POWER: Power the device on or off
- INFO: Displays detailed timings of video input and output. Also displays firmware version
- KEYPAD / 0-9: Selects AV source and input format. See remote picture on the side for reference
- MENU: Activates/deactivates OSD menu
- OK: Selects sub-menu or function
- BACK: Returns to previous menu level or from info page to normal source display page
- UP/DOWN: Selects next/previous menu option or next/previous input when not in menu
- LEFT/RIGHT: Option value -/+
- OSD: Switches between different OSD modes (Full, SImple, Off)
- P-LM, A-LM, SCL: Select respective operating mode
- LM.MODE: Select multiplication target for LM modes
- LM.DIL: Select deinterlace mode (Bob / Noninterlace restore) for LM
- SCRSHOT: Reserved for future use
- P.LOAD: Open a menu to load profile
- SL.INT+/-: Hotkeys for adjusting scanline strength
- SL.MODE: Hotkey for scanline mode selection
- SL.TYPE: Hotkey for selecting next "Scanline type" option value
- SL.ALIGN: Hotkey for scanline alignment selection
- PHASE+/-: Hotkeys for sample phase adjustment
- P1-9: Reserved for future use
- SCL.RES: Scaler output resolution selection
- SCL.FL: Scaler framelock selection
- SCL.S.ALG: Scaler scaling algorithm selection
- SCL.D.ALG: Scaler deinterlace algorithm selection
- SCL.AR: Scaler aspect ratio selection
- SCL.ROT: Reserved for future use
- SCL.ZOOM: Open scaler size adjustment menu
- SCL.PAN: Open scaler position adjustment menu
It is also possible to operate OSSC Pro using L336 remote of original OSSC. More details here.
PCB buttons
- BTN: Enter / exit menu
- JOY: 4-directional joystick switches input or test pattern mode when not in menu. Inside menu it provides navigation with the added push function to enter sub-menus
Status LEDs
- Green: Power on. Temporarily off when IR remote code detected
- Red: Standby indicator. When device is on, red LED flashing indicates resyncing to input
- Blue: Framelock
Fan
An optional 40x10mm 5V fan can be installed on the case to reduce FPGA temperature. PWM is supported and can be adjusted from the options. A reference model is Noctua NF-A4x10 5V PWM.
Getting started
Turn on the board by pressing power button on remote or by holding the on-board button for a couple seconds. A 480p test pattern should show up in the monitor. Turn on the video source and select correct input.
The firmware has 2 primary operating modes: line multiplier and scaler. Line multiplier is reminiscent of classic line doublers and OSSC while scaler works more like video processors like VP50 or Framemeister. In general scaler mode offers more flexibility and easier usage via fixed output resolution and (optionally) fixed refresh rate. Some users may prefer to stay with strict multiplication to preserve the original look as much as possible, though. The mode can be switched from "Output opt -> Operating mode" on the menu. Main menu has matching sub-menus for each of the 2 operating modes which are accessible even if the said operating mode is not active. Most important properties of these modes are listed in the table below.
| Pure LM | Adaptive LM | Scaler – framelock | Scaler - no framelock | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latency | max 2 lines | Max 60 lines | ~1 frame | 1-2 frames |
| Display compatibility | Variable | Very high | Very high | Full |
| Deinterlace alg. | Bob, Noninterlace restore | Bob, Noninterlace restore | Bob, Weave, Motion adaptive | Bob, Weave, Motion adaptive |
| Scaling alg. | X: oversample, integer; Y: integer | X: oversample, integer; Y: integer | X: oversample, polyphase; Y: polyphase | X: oversample, polyphase; Y: polyphase |
| Input mode switch delay | Very fast | Very fast | Fast | Instant* |
| Transformations | Pan | Pan | Zoom, Pan, (Rotate) | Zoom, Pan, (Rotate) |
| Postprocessing opt. | Scanlines, Border, Masks | Scanlines, Masks | Scanlines, Masks, BFI | Scanlines, Masks, BFI |
* guaranteed only when Scaling algo is not integer and Aspect is not Auto or 1:1 PAR
Test pattern
In test pattern mode it is possible to test all output presets on a display. To change preset, press <- or -> from remote or front panel joystick while in test pattern mode.
Settings
Input select
Selects the source, see #AV inputs
AV1-3 video in opt.
Video LPF
Video low-pass filter. Filters out high-frequency noise on video.
- Auto: Suitable LPF is automatically selected based on source mode [default]
- 9-450MHz: Video bandwidth is limited to selected frequency
Reverse LPF
Compensates unintended LPF/bleeding caused by sub-optimal video DAC (e.g. 1st rev SNES consoles) or long cables.
- 0-31: Reverse LPF strength. [default=0]
YPbPr input Color Space
Controls YPbPr->RGB colorspace conversion coefficients.
- Auto: Input colorspace is selected based on resolution. [default]
- Rec. 601: Input is assumed to be in Rec. 601 format, which is generally true for SD video.
- Rec. 709: Input is assumed to be in Rec. 709 format, which is generally true for HD video.
R/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb offset
Fine-adjustment of Red/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb channel offset (brightness).
- 0-1023: [default=512]
R/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb gain
Fine-adjustment of Red/Pr / G/Y / B/Pb channel gain (contrast).
- 0-1023: [default=324]
Clamp strength
Sets the strength of backporch clamp.
- 0-7: [default=7]
Clamp/ALC position
Sets the position of backporch clamp (in percentage of line length).
- 0.1-25%: [default=0.7%]
Clamp width
Sets the width of backporch clamp pulse (in percentage of line length).
- 0.1-10%: [default=2.5%]
Clamp/ALC on coast
Sets whether clamp/ALC is enabled during coast.
- On: Clamp/ALC enabled during coast. [default]
- Off: Clamp/ALC disabled during coast.
Auto level ctl (ALC)
Sets whether ALC is enabled.
- On: ALC enabled. [default]
- Off: ALC disabled.
ALC V filter
ALV vertical filter coefficient. Reduce from default if line/field tilt occurs.
- 32-4096 lines: [default=512 lines]
ALC H filter
ALV horizontal filter coefficient (duration for which ALC is applied after clamp).
- 16-128 pixels: [default=16 pixels]
Lumacode
Enables Lumacode decoding for selected system. A Lumacode source is connected to Y RCA jack and uses AV2_RGsB logical input. You need to additionally select sampling preset for the target system, and possibly adjust phase and G/Y offset to get colors right.
- Off: Lumacode decoding disabled [default]
- C64: Lumacode decoding enabled for C64.
- Spectrum: Lumacode decoding enabled for ZX Spectrum.
- Coleco / MSX: Lumacode decoding enabled for Colecovision / MSX1.
- Intellivision: Lumacode decoding enabled for Intellivision.
- NES: Lumacode decoding enabled for NES. Use "SNES 256col" sampling preset.
- Atari GTIA: Lumacode decoding enabled for Atari 8bit home computers. Use Line3x/4x/6x-320col mode with H. samplerate of 456.
- Atari VCS: Lumacode decoding enabled for Atari 2600 (VCS). Use Line4x-320col mode with H. samplerate of 456.
Lumacode palette set
Selects palette set for Lumacode modes
- PAL: Palette matching PAL machines [default]
- Custom: Select loaded custom palette set (see next option)
Custom Lumacode palette set
Open menu for loading .txt file for custom palette set consisting of palettes for one or multiple supported sources. The file needs to be placed on lumacode/ subfolder on SD root. Click Expand on the right to view example config file containing all source entries.
c64_pal 000000,2a1b9d,7d202c,84258c,4c2e00,3c3c3c,646464,4fb3a5,7f410d,6351db,939393,bfd04a,339840,b44f5c,7ce587,ffffff zx_pal 000000,000000,0200FD,CF01CE,0100CE,CF0100,FF02FD,01CFCF,FF0201,00CF15,02FFFF,FFFF1D,00FF1C,CFCF15,CFCFCF,FFFFFF msx_pal 000000,5455ed,fc5554,ff7978,000000,d4524d,7d76fc,42ebf5,21b03b,21c842,ff7978,cccccc,c95bba,d4c154,e6ce80,ffffff intv_pal 0c0005,a7a8a8,fffcff,ff3e00,ffa600,faea27,00780f,00a720,6ccd30,002dff,5acbff,bd95ff,c81a7d,ff3276,3c5800,c9d464 nes_pal 000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,000000,626262,001fb2,2404c8,5200b2,730076,800024,730b00,522800 244400,005700,005c00,005324,003c76,000000,ababab,0d57ff,4b30ff,8a13ff,bc08d6,d21269,c72e00,9d5400,607b00,209800 00a300,009942,007db4,000000,ffffff,53aeff,9085ff,d365ff,ff57ff,ff5dcf,ff7757,fa9e00,bdc700,7ae700,43f611,26ef7e 2cd5f6,4e4e4e,ffffff,b6e1ff,ced1ff,e9c3ff,ffbcff,ffbdf4,ffc6c3,ffd59a,e9e681,cef481,b6fb9a,a9fac3,a9f0f4,b8b8b8 tia_pal 000000,404040,6C6C6C,909090,B0B0B0,C8C8C8,DCDCDC,ECECEC,444400,646410,848424,A0A034,B8B840,D0D050,E8E85C,FCFC68 702800,844414,985C28,AC783C,BC8C4C,CCA05C,DCB468,ECC878,841800,983418,AC5030,C06848,D0805C,E09470,ECA880,FCBC94 880000,9C2020,B03C3C,C05858,D07070,E08888,ECA0A0,FCB4B4,78005C,8C2074,A03C88,B0589C,C070B0,D084C0,DC9CD0,ECB0E0 480078,602090,783CA4,8C58B8,A070CC,B484DC,C49CEC,D4B0FC,140084,302098,4C3CAC,6858C0,7C70D0,9488E0,A8A0EC,BCB4FC 000088,1C209C,3840B0,505CC0,6874D0,7C8CE0,90A4EC,A4B8FC,00187C,1C3890,3854A8,5070BC,6888CC,7C9CDC,90B4EC,A4C8FC 002C5C,1C4C78,386890,5084AC,689CC0,7CB4D4,90CCE8,A4E0FC,003C2C,1C5C48,387C64,509C80,68B494,7CD0AC,90E4C0,A4FCD4 003C00,205C20,407C40,5C9C5C,74B474,8CD08C,A4E4A4,B8FCB8,143800,345C1C,507C38,6C9850,84B468,9CCC7C,B4E490,C8FCA4 2C3000,4C501C,687034,848C4C,9CA864,B4C078,CCD488,E0EC9C,442800,644818,846830,A08444,B89C58,D0B46C,E8CC7C,FCE08C gtia_pal 000000,111111,222222,333333,444444,555555,666666,777777,888888,999999,aaaaaa,bbbbbb,cccccc,dddddd,eeeeee,ffffff 091900,192806,29370d,3a4714,4a561b,5a6522,6b7529,7b8430,8c9336,9ca33d,acb244,bdc14b,cdd152,dee059,eeef60,ffff67 300000,3d1108,4b2211,593319,674422,75552a,826633,90773b,9e8844,ac994c,baaa55,c7bb5d,d5cc66,e3dd6e,f1ee77,ffff80 4b0000,570f0c,631e18,6f2e24,7a3d30,874d3c,935c49,9f6b55,ab7b61,b68a6d,c39a79,cfa986,dbb892,e6c89e,f3d7aa,ffe7b7 550000,600e10,6b1c21,772a32,823843,8d4654,995465,a46276,af7187,bb7f98,c68da9,d19bba,dda9cb,e8b7dc,f3c5ed,ffd4fe 4c0047,570d53,631b5f,6f286b,7b3678,874384,935190,9f5e9c,ab6ca9,b779b5,c387c1,cf94cd,dba2da,e7afe6,f3bdf2,ffcbff 30007e,3b0b85,49198d,572796,65349f,7242a7,8050b0,8e5db8,9c6bc1,a979c9,b786d2,c594db,d3a2e3,e0afec,eebdf4,fccbfd 0a0097,1a0e9d,2a1da4,3b2cab,4b3ab2,5b49b9,6c58c0,7c67c7,8c75ce,9c84d5,ad93dc,bda2e3,ceb0ea,debff1,eecef8,ffddff 00008e,0c0d94,1b1e9c,2a2ea3,393eab,484eb2,575eba,666ec1,747ec9,838fd0,929fd8,a1afdf,b0bfe6,bfcfee,cedff5,ddeffd 000e64,0c1e6e,192e78,263e83,324e8d,3f5e97,4c6ea2,587eac,658eb6,729ec1,7eaecb,8bbed5,98cee0,a4deea,b1eef4,beffff 002422,09302e,153f3d,204d4c,2c5c5a,376a69,427978,4e8786,599695,65a4a4,70b3b2,7cc1c1,87d0d0,92dfde,9eeded,a9fcfc 003200,0b3f0e,164d1c,225b2b,2d6839,397648,448456,509164,5b9f73,67ad81,72ba90,7ec89e,89d6ac,95e3bb,a0f1c9,acffd8 003400,0c410a,194f14,265c1e,336a28,407732,4c853c,599246,66a050,73ad5a,80bb64,8cc86e,99d678,a6e382,b3f18c,c0ff97 002a00,0f3807,1e460e,2d5416,3c621d,4b7124,5a7f2c,698d33,799b3b,88a942,97b849,a6c651,b5d458,c4e260,d3f067,e3ff6f 0d1700,1d2606,2d350d,3d4514,4d541b,5d6422,6d7329,7d8330,8e9237,9ea23e,aeb145,bec14c,ced053,dee05a,eeef61,ffff68 330000,401008,4e2111,5b321a,694323,77542c,846535,92763e,9f8646,ad974f,bba858,c8b961,d6ca6a,e3db73,f1ec7c,fffd85
AV1-3 sync opt.
Analog sync Vth
Sets the sync slicer threshold for video-level sync. May need adjustment if source sync level is not typical and dropouts occur.
- 0-300mV: threshold voltage. [default=120mV]
TTL Hsync Vth
Sets the sync slicer threshold for TTL level sync. May need adjustment if source sync level is not typical and dropouts occur.
- 400-3205mV: threshold voltage. [default=1148mV]
Analog sync pre-STC
Sets sync tip clamp LPF.
- Off
- On (5MHz LPF) [default]
- On (2.5MHz LPF)
- On (0.5MHz LPF)
Sync glitch filt len
Sets the sync glitch filter length. May need to be increased if there are glitches around sync pulses.
- 37-592ns: filter length. [default=111ns]
H-PLL Pre-Coast
Defines when PLL coast (current freq. freeze) is activated.
- 0-5 lines: Number of scanlines before vsync at when coast is activated. [default=4]
H-PLL Post-Coast
Defines when PLL coast (current freq. freeze) is deactivated.
- 0-5 lines: Number of scanlines after vsync at when coast is deactivated. [default=4]
H-PLL Loop Gain
Adjusts loop gain of H-PLL which affects sampling clock stability. A higher value makes the PLL react fast to changes in hsync interval which may make sampling more accurate but at the cost of increased jitter in output pixel clock. A small value ensures best compatibility, but sync jitter in the source (e.g. SNES) may result to sampling jitter on nearby scanlines. Increase for sources with sync jitter if your display is able to tolerate jitter in output clock.
- 0-3: [default=0]
Ext. dotclk range
Extended input dotclk range to enable exceeding ADC sampling rate spec.
- Off: Disabled. [default]
- On: Setting required e.g. for 1920x1440_60 with reduced blanking. Might have adverse effects like slightly higher sampling jitter with other modes.
AV4 video in opt.
Default RGB range
Selects the assumed RGB range if source does not explicitly specify it in metadata.
- Limited: Limited range as per CEA spec. [default]
- Adaptive: Full-range RGB.
Pixel decimation
Enforces pixel decimation for sources with pixel repetition or multiplied horizontal resolution.
- Auto: Decimation follows metadata. [default]
- 1-10: Manual override
Enables dynamic reduction of pixel decimation factor when menu flag is set in metadata (Mister DV1 mode).
- Off: Horizontal resolution is kept same regardless of menu flag.
- On: Horizontal decimation is reduced when menu flag is set to improve overlay readability. [default]
EDID selection
Selects EDID to AV4 port. New EDID is activated during boot or when AV4 input is activated.
- Default: Default EDID indicating maximum supported AV capability of OSSC Pro.[default]
- 2ch audio: EDID where HDMI LPCM audio support is limited to 2.0ch. Useful with sources like PS4 which assign audio channel count based on EDID and do not offer full customization.
- 10bpc RGB+HDR: EDID where 10bpc Deep Color and HDR support have been enabled. Useful for HDR bypass. Note: OSSC Pro converts signal to 8bpc and is only capable of flagging output as HLG, thus some loss of precision is likely to occur.
- 720p max.: EDID where indicated maximum resolution support is limited to 720p. Useful for LM downscaling (line drop) purposes.
- Custom: Custom EDID loaded from SD card.
Custom EDID load
Opens a menu to load custom EDID file (edid/*.bin) from SD card. Up to 3 extension headers are support (i.e. max EDID size is 512 bytes).
Line multiplier opt
Line multiplier mode
Selects how line multiplier mode operates.
- Pure: All lines are multiplied for output, operation like original OSSC. Mainly for backwards compatibility.
- Adaptive: Visible lines are multiplied while amount of blanking lines is adjusted to match selected standard output resolution. [default]
Deinterlace mode
Selects how interlaced content is processed in line multiplier modes.
- Bob: Displays fields one after another with even field being offset by half input line, resembling how interlaced content looks on a CRT. [default]
- Noninterlace restore: Displays fields one after another without any offset by default. Useful for 240p games running in 480i (e.g. classic game collections).
NI restore Y offset
Offsets even field in noninterlace restore mode.
- 0: No offset for even field. [default]
- 1: Even field is offset by a full input line. Needed depending on field order of 240p->480i conversion.
256x240 aspect
Selects the output aspect for 256x240 sampling presets.
- Pseudo 4:3 DAR: Integer-multiplication is handled so that target aspect is close to 4:3. [default]
- 1:1 PAR: Maintains square pixel aspect ratio.
Pure LM opt.
Refer to OSSC#Output_opt..
Adaptive LM opt.
<input_mode> proc
Selects how <input_mode> is processed via output resolution and line multiplication factor.
<input_mode> mode
Selects a sampling preset for <input_mode>.
P-LM Adv. timing
Refer to OSSC#Advanced_timing_tweaker.
A-LM Adv. timing
Allows editing of sampling/output parameters. Sampling preset to edit (default is current mode) is changed via LEFT/RIGHT keys and selected via OK key which then opens editor menu.
Clock & Phase
Enter to fine-tune sampling clock and phase via arrow keys. Only for advanced users.
Size / crop
Enter to adjust bounding box size for input signal (active area) via arrow keys. In scaler mode the active window is scaled to full screen (unless in integer scale mode), effectively resulting to zooming in/out. In A-LM this results to cropping instead.
Position
Enter to adjust bounding box position for input signal via arrow keys.
Reset preset
Resets parameters of selected preset to default values.
Scaler opt.
DFP output mode
Selects output mode for Digital Flat Panel (DFP). Supported output refresh range is shown in braces.
- 720x480 (60Hz): Standard 480p output supported by all HDTVs.
- 720x480 WS (60Hz): Standard widescreen 480p output supported by all HDTVs.
- 720x576 (50Hz): Standard 576p output supported by most HDTVs.
- 720x576 WS (50Hz): Standard widescreen 576p output supported by most HDTVs.
- 1280x720 (24-240Hz): Standard 720p output supported by majority of HDTVs.
- 1280x1024 (24-150Hz): SXGA mode for 5:4 desktop monitors.
- 1920x1080i (48-120Hz): Standard 1080i output supported by most modern HDTVs.
- 1920x1080 (24-120Hz): Standard 1080p output supported by all modern HDTVs. [default]
- 1600x1200 (24-100Hz): UXGA mode for 4:3 desktop monitors.
- 1920x1200 (24-100Hz): WUXGA mode for 16:10 desktop monitors. Uses CVT timings (RB for 60Hz).
- 1920x1440 (24-90Hz): 4:3 1440p mode for compatible displays. Uses CVT timings (RB for 60Hz).
- 2560x1440 (24-72Hz): 16:9 1440p mode for compatible displays. Uses CVT-RB timings.
- 2880x2160 (24-60Hz): 4:3 2160p mode for compatible displays. Uses CVT-RB timings and 2x pixel repetition.
CRT output mode
Selects output mode for CRT. Modes are meant for video DACs, not HDMI devices. Supported output refresh range is shown in braces.
- 240p (24-240Hz): Non-interlaced 60Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs. [default]
- 240p WS (24-240Hz): Non-interlaced 60Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 288p (24-250Hz): Non-interlaced 50Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 288p WS (24-250Hz): Non-interlaced 50Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 480i (48-180Hz): Interlaced 60Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 480i WS (48-180Hz): Interlaced 60Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 576i (48-150Hz): Interlaced 50Hz SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 576i WS (48-150Hz): Interlaced 50Hz widescreen SD mode for 15kHz capable CRT TVs.
- 480p (24-170Hz): 480-line mode for 31kHz capable CRT monitors.
- 540p (24-180Hz): 540-line mode for 1080i capable HD-CRT TVs.
- 1024x768 (24-240Hz): XGA mode for CRT monitors.
- 1280x960 (24-160Hz): QuadVGA mode for CRT monitors.
- 2048x1536 (24-60Hz): QuadXGA mode for CRT monitors or tablet displays.
Output type
Selects which one of the 2 above mode lists is used.
- DFP: Output to Digital Flat Panel via HDMI. [default]
- CRT: Output to CRT via HDMI-VGA/SCART converter.
Framelock
Defines output refresh rate and how it is generated.
- On: Output refresh rate is locked to input. Minimizes latency, but any interruption in input (e.g. video mode change) may temporarily break sync on output side. [default]
- Off (source Hz): Output refresh rate is not directly generated from input, but using an external clock source instead. Refresh rate is set to match input as closely as possible.
- Off (preset Hz): Output refresh rate is taken from the output preset, see #Adv. disp timing
- Off (50Hz): Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 50Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting.
- Off (60Hz): Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 60Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting.
- Off (100Hz): Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 100Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting.
- Off (120Hz): Output refresh rate is not generated from input. Output is 120Hz if supported by the selected output resolution setting.
Framelock multiplier
Enables refresh rate multiplication in framelocked mode.
- 1-10x: Refresh rate multiplier. Be aware of above output rate limits as exceeding it results to falling back into highest refresh preset without framelock.[default=1x]
Aspect ratio
Selects aspect ratio for the source.
- Auto: Selects aspect ratio based on sampling preset. [default]
- 4:3: Standard aspect ratio for most classic console and home computer sources.
- 16:9: Widescreen aspect ratio for consoles/games supporting widescreen.
- 8:7: Special aspect ratio for square pixels with NES/SNES. Most useful with their respective sampling presets.
- 1:1 source PAR: Source is assumed to have 1:1 pixel aspect ratio. Use only with non-generic sampling presets.
- Full: Source is assumed to have same aspect ratio as selected output resolution, i.e. it will be scaled to fit screen both horizontally and vertically.
Scaling algorithm
Selects scaling algorithm/filter applied for the polyphase scaler engine. The engine supports edge-adaptive scaling which is able to use different filter for parts of the picture which are detected as edges. Edge-adaptive modes are denoted with '&' which is followed by the filter used for edge content.
- Auto: Uses Nearest for low-res sources and Lanczos3_sharp for med/high-res. [default]
- Integer (underscan): Integer scaling with underscan priority (in case a small part of picture would be otherwise cut). Mainly usable with non-generic sampling presets.
- Integer (overscan): Integer scaling with overscan priority (in case a small part of picture would be otherwise letter/pillarboxed). Mainly usable with non-generic sampling presets.
- Nearest: Nearest neighbor scaling algorithm. Most appropiate for 2D pixel graphics where more sophisticated filters may add noticeable blur / ringing.
- Lanczos3: High-quality scaling algorithm suitable for general video material and 3D graphics.
- Lanczos3_sharp: Sharpened version of Lanczos3 algorithm.
- Lanczos3&3_sharp: Sharpened version only applied for edges.
- Lanczos4: Similar to Lanczos3 but with reduced smoothening.
- GS sharp: General scaling with sharp interpolation.
- GS medium: General scaling with medium-sharp interpolation.
- GS soft: General scaling with soft interpolation.
- Custom: Select loaded custom configuration (see next option)
Custom SCL alg
Opens a menu to load custom scaler algorithm configuration file (scl_alg/*.cfg) from SD card. A configuration file consists of 2 or 4 lines in the format below. 2 first lines define scaling algorithm for X/Y direction. 2 extra lines can be optionally added to enable edge-adaptive mode and set X/Y scaling algorithm for edge content. Each line either names a preset algorithm (nearest, lanczos3, lanczos3_13, lanczos4, gs_sharp, gs_medium, gs_soft) or defines a filename for custom coefficient .txt file placed on the same folder. Custom coefficients must be in Mister format and define 64 phases (both 9bit & 10bit coeffs are supported).
X Y (edge: X) (edge: Y)
Edge threshold
Sets edge-detection threshold for edge-adaptive scaling algorithms.
- 0-255: [default=7]
Deinterlace mode
Selects the deinterlace mode for interlaced sources.
- Bob: Displays fields one after another with even field being offset by half input line, resembling how interlaced content looks on a CRT. Works well with fast-moving content.
- Weave: Interleaves lines from 2 adjacent fields. Good for static content.
- Motion adaptive: . Uses Bob for moving areas of the picture and weave for static ones. [default]
Motion shift
Sets motion detection threshold for motion adaptive deinterlacer.
- 0-7: [default=3]
Generic samplerate
Selects preference for sampling rate in generic modes.
- Auto: . Sampling rate is selected based on output mode width. Little or no additional scaling in X-direction is needed. [default]
- Lowest: Lowest available generic sampling preset is used (active width typically 720). Selected scaling algorithm has major impact on X-direction upscaling.
- Highest: Highest available generic sampling preset is used (active width around 2000). Selected scaling algorithm has major impact on (typically) X-direction downscaling.
240p/288p mode
Selects sampling preset for 240p/288p "15kHz" sources.
350-400p mode
Selects sampling preset for 350-400p "~24kHz" sources.
480i/576i mode
Selects sampling preset for 480i/576i "15kHz" interlaced sources.
480-512p mode
Selects sampling preset for 480-512p "31kHz" sources.
576p mode
Selects sampling preset for 576p "31kHz" sources.
Adv. timing
Refer to #A-LM Adv. timing.
Output opt.
Operating mode
Selects operating mode of the device. Respective sub-menus under main menu have detailed options for each operating mode
- Line multiplier: Operates in basic line multiplication mode. [default]
- Scaler: Operates in more flexible scaler mode.
Test pattern mode
Selects video mode for test pattern. May be used to test display compatibility.
- 240p...2880x2160_60: Output video mode. [default=480p]
TX mode
Sets the output TX mode.
- HDMI (RGB Full): 24-bit full range RGB output with audio and auxiliary Infoframe packets. [default]
- HDMI (RGB Limited): 24-bit limited range RGB output with audio and auxiliary Infoframe packets.
- HDMI (YCbCr444): 24-bit YCbCr 4:4:4 (Rec. 601) output with audio and auxiliary Infoframe packets.
- DVI: 24-bit full range RGB output. Required if target display does not support HDMI.
HDMI HDR flag
Setups HDR Infoframe to indicate HDR output with HLG gamma when in HDMI TX mode.
- Off: Default SDR output. [default]
- On: Output is flagged as HDR HLG. Gamma response is not corrected so some accuracy is lost.
HDMI VRR flag
Setups VRR metadata to spoof VRR output (vertical blank is not extended dynamically).
- Off: No VRR metadata sent. [default]
- Freesync: Freesync infoframe sent.
HDMI combined sync
Enables RGBS output from HDMI port when using HDMI to VGA DACs.
- Off: Standard HV sync output. [default]
- On: Combined sync output.
CSync combiner
Selects sync combiner type for HDMI and Extra AV output csync output.
- Type A (AND): H+V sync are combined with AND logic. Falling hsync edges in consistent position except during VSYNC when not present. [default]
- Legacy (XNOR): Falling hsync edges present also during VSYNC but with some offset in position.
Full TX setup
Sets whether TX initialization is done every time a video mode changes.
- Off: TX is kept on during mode changes. [default]
- On: TX is reinitialized when input/output mode changes, resulting to a short blank. Needed if display permanently loses picture / audio upon video mode changes.
1080p120 preset
Selects timings to be used for 1080p120 output. Compatibility varies between boards and displays.
- CVT-RB: Standard reduced blanking CVT mode. [default]
- Min. blank: Blanking is pushed to minimum in order to reduce pixel clock further, but at the price of insufficient space for audio data.
- CEA-861: CEA-861 compatible mode which has highest display compatibility but also highest pixel clock. Video stability is not guaranteed on all boards, especially without active cooling.
- CEA-861 PR2x: CEA-861 compatible mode which is guaranteed to work on all boards and displays with HDMI 120Hz support. However, 2x pixel repetition is used.
2160p60 preset
Selects timings to be used for 2160p60 output. Compatibility varies between boards and displays.
- CVT-RB PR2x: Standard reduced blanking CVT mode with 2x pixel repetition. [default]
- Min. blank: Blanking is pushed to minimum in order to reduce pixel clock further, but at the price of insufficient space for audio data. 2x pixel repetition is used.
Adv. disp timing
Allows changing output preset parameters. Useful mainly for users of CRTs (overscan mitigation) and HD-Ready LCDs/PDPs with native resolutions not covered by existing presets. Can be also used to test display refresh rate limits in test pattern mode, or set custom refresh rate for SCL Framelock off (preset Hz) mode.
Reset disp preset
Resets parameters for currently active (or one selected under "Adv. disp timing") preset.
Audio opt.
Sampling format
Sets sampling format for analog audio input.
- 24bit/48kHz: Standard format supported by all displays. [default]
- 24bit/96kHz: 96kHz sampling rate
- 24bit/192kHz: high 192kHz sampling rate. May not work with reduced blanking output modes.
Quad stereo
Generates multichannel LPCM audio output where stereo signal is copied into rear speakers.
- Off: Standard 2.0 channel format. [default]
- On (4.0): 4.0 channel format.
- On (5.1): 5.1 channel format.
- On (7.1): 7.1 channel format.
Pre-ADC gain
Volume gain adjustment before audio is digitized. Can be used to compensate level differences between sources.
- -12-+12dB: Gain. [default=0dB]
AV1 audio source
Selects audio source for AV1 video input.
- AV1 (analog): AV1 audio (SCART). [default]
- AV2 (analog): AV2 audio (2x RCA jacks).
- AV3 (analog): AV3 audio (3.5mm jack).
- SPDIF: Digital toslink audio input.
AV2 audio source
Selects audio source for AV2 video input.
- AV2 (analog): AV2 audio (2x RCA jacks). [default]
- AV3 (analog): AV3 audio (3.5mm jack).
- SPDIF: Digital toslink audio input.
AV3 audio source
Selects audio source for AV3 video input.
- AV2 (analog): AV2 audio (2x RCA jacks).
- AV3 (analog): AV3 audio (3.5mm jack). [default]
- SPDIF: Digital toslink audio input.
AV4 audio source
Selects audio source for AV4 video input. "AV1 (analog)", "AV2 (analog)", "AV3 (analog)", "SPDIF", "AV4 (digital)"
- AV2 (analog): AV2 audio (2x RCA jacks).
- AV3 (analog): AV3 audio (3.5mm jack).
- SPDIF: Digital toslink audio input.
- AV4 (digital): Digital HDMI audio. [default]
EXP audio source
Selects audio source for Legacy AV Input expansion.
- AV2 (analog): AV2 audio (2x RCA jacks). [default]
- AV3 (analog): AV3 audio (3.5mm jack).
- SPDIF: Digital toslink audio input.
3.5mm jack assign
Selects function on 3.5mm jack
- AV3 input: The jack functions as audio input for AV3. [default]
- AV1 output: Audio from SCART input is routed to the jack, e.g. enabling analog passthru to AVR.
Scanline opt.
Scanlines
Controls whether emulated scanlines are drawn on top of the picture
- Off: No scanlines drawn [default]
- Auto: Horizontal scanlines are drawn for 240p/288p sources, alternating scanlines are enabled for 480i/576i, no scanlines for other sources
- On: Scanlines are drawn for every source according to "Scanline type" option
Sl. strength
- 6-100%: Strength of the emulated scanlines [default=6%]
Sl. hybrid str
- 0-175%: Strength of hybrid/blend effect (depedence of the pixel that is overlayed) in scanlines [default=0%]
Sl. method
Selects the method how scanlines are generated.
- Multiplication: Scanline is generated by multiplying source RGB value [default]
- Subtraction: Scanline is generated by subtracting from source RGB value
Sl. LM Bob altern.
Controls whether scanline position alternates along with fields of Bob deinterlaced LM modes.
- Off: Scanlines are always mapped to same output lines.
- On: Position is tied to field which shows as alternating position in output. Useful for reducing flicker. [default]
Sl. alignment
- Top: Scanline is drawn on top position of every group of output lines formed from a single input line. [default]
- Bottom: Scanline is drawn on bottom position of every group of output lines formed from a single input line.
Scanline type
- Horizontal: Scanline pattern is drawn on every N output lines (value of N depends on processing mode). [default]
- Vertical: Scanline pattern is drawn on every M output column (value of M depends on processing mode).
- Horiz. + Vert.: Combination of horizontal and vertical mode.
- Custom: Scanlines are drawn accoring to line-wise and column-wise strength set under Custom Sl.
Custom Sl.
Enables separate setting of each overlay line and column (line strength takes priority on pixels where it is >0%).
H interval
Sets the horizontal interval (in output pixels) in which the column overlay pattern is repeated.
V interval
Sets the vertical interval (in output lines) in which the line overlay pattern is repeated.
Sub-line M str
Strength for Mth sub-line, 0% disables line overlay.
Sub-column N str
Strength for Nth sub-column, 0% disables column overlay.
Post-proc.
Border color
Sets border color
- Black|Blue|Green|Cyan|Red|Magenta|Yellow|White: Border color. [default=Black]
Border brightness
Sets border brightness (only effective is color is set to non-black). Could be used as a precaution with self-emissive displays to avoid uneven wear.
- 0-15: Border brightness level. [default=8]
Shadow mask
Enables a mask pattern imitating CRT shadow mask.
- Off: Mask pattern disabled. [default]
- A-Grille: Mask imitating aperture grille found in Trinitron monitors.
- TV: Mask imitating shadow mask in consumer TVs.
- PVM: Mask imitating Sony PVM series.
- PVM-2530: Mask imitating Sony PVM-2530.
- XC-3315C: Mask imitating Mitsubishi XC-3315C.
- C-1084: Mask imitating classic Commodore 1084 personal monitor.
- JVC: Mask imitating generic JVC monitor.
- VGA: Mask imitating generic VGA monitor.
- Custom: Select loaded custom shadow mask (see next option)
Custom shadow mask
Opens a menu to load custom shadow mask file (shmask/*.txt) from SD card. The file must be in Mister format.
Sh. mask strength
- 6-100%: Strength of the selected shadow mask[default=100%]
BFI for duplicated frames
Enables black frame insertion feature for modes with framelock multiplier >1x. Reducing image persistence can be used to improve motion resolution at the cost of some flicker.
- After N src frames: BFI is enabled for remaining duplicates after showing original frame N times.
- Off: BFI disabled. [default]
BFI strength
Sets the strength of BFI for frames its applied to. Can be used to trade off motion resolution for improved brightness / reduced flicker
- 6-100%: Sets opaqueness of the black mask applied over a duplicated frame. [default=100%]
Expansion opt.
Expansion select
Selects active expansion card
- Auto: Automatically detected. [default]
- Off: No expansion card inserted
- Extra AV out: Extra AV out expansion
- Legacy AV in": Legacy AV in expansion
- UVC bridge": Reserved for future use
Extra AV out mode
Sets the mode for extra_av_out expansion card
- Off: No output on extra_av_out [default]
- RGBHV: Normal RGBHV output via VGA
- RGBCS/RGBS: Normal RGBCS output via VGA or RGBs via an adapter
- RGsB: Sync-on-green RGB output
- YPbPr: YPbPr output
Legacy AV opt.
Sets various options for this expansion card
Signal information
Displays information about input & output timings, firmware and uptime.
Settings
Power-up state
Selects the operational state which is activated when power supply is connected.
- Standby: Unit is placed in standby mode. [default]
- Active: Unit is placed in active mode.
Initial input
Sets the input which is automatically activated when device is powered on. Test pattern is displayed regardless of initial input setting until sync is detected on the respective input.
OSD
Selects whether OSD rendering is enabled and in which mode. When enabled, Navigation OSD is permanently visible when menu is active and a status OSD is temporarily displayed when input video mode changes.
- Off: OSD is not displayed.
- Full: Full OSD is displayed. [default]
- Simple: Simple OSD is displayed.
OSD status display
Selects how long updated video parameters are shown on the status OSD.
- 2s: status shown for 2 seconds.
- 5s: status shown for 5 seconds. [default]
- 10s: status shown for 10 seconds.
- Off: Status is not displayed.
OSD cursor color
Sets highlight color for OSD
- Green|Cyan|Red|Magenta|Yellow: Highlight color. [default=Yellow]
Fan PWM
Sets speed for the optional fan accessory
- 0-100%: PWM duty cycle. [default=0%]
Led PWM
Sets intensity for front panel status LEDs
- 10-100%: PWM duty cycle. [default=50%]
Bind IR remote
Learns keycodes from an IR remote. Press prompted function key on a new remote and confirm it by pressing the key again. Once all functions have been configured, new keymap settings are saved. Notes:
- Any unused functions can be bound to a single unused key
- If you entered a wrong key, press PCB button to go back to setup of previous function.
- To clear custom bindings and reset to default - Choose the "Bind IR remote" option and then immediately press the PCB button (the circle shaped button) on the front of the OSSC. This will cancel setup of the new remote and prompt if ther default keymap should be loaded. Press the navigation control on the front of the OSSC Pro to the right to confirm and reset to default.
Load profile
Loads selected profile slot from on-board flash. Slot 0 is loaded automatically at power-up. Use P.LOAD hotkey for paged profile browsing.
Save profile
Saves profile into selected slot in on-board flash. Settings (i.e. contents of settings menu which are not part of a profile) are saved simultaneously. Profile name to be written can be overridden by prof_n_i.txt on SD card root (one line per profile, max. 17 chars per name, see "How to rename profiles" below for more information).
SD Load profile
Loads selected profile slot from SD card. Use P.LOAD hotkey for paged profile browsing.
SD Save profile
Saves profile into selected slot on SD card. Settings (i.e. contents of settings menu which are not part of a profile) are saved simultaneously to SD card on a separate file. Profile name to be written can be overridden by prof_n.txt on SD card root (one line per profile, max. 17 chars per name, see "How to rename profiles" below for more information ).
Reset profile
Resets current profile to default values without saving it.
Fw. update
Firmware update function. New version is displayed on the screen after which update can be initiated by pressing "->" via remote or PCB joystick. Below are descriptions for error codes which may prevent the upgrade process.
- Error -1: SD card not detected.
- Error -2: FW file not found. Rename the file as ossc_pro.bin and ensure it's on the root of the SD card. If active firmware is v0.75 or below, make also sure SD card is formatted as FAT32.
- Error -3...-5: FW header error. The firmware file is corrupted.
- Error -6: Target offset not aligned to flash sector. Firmware file contains invalid offset.
- Error -7: Image exceeds flash boundary. Firmware file is too large for the flash.
- Error -8: FW data read error. Error while copying the firmware file to DRAM.
- Error -9: CRC error while checking the data copied to DRAM. Change to test pattern or restart the device, and try again.
How to rename profiles
To give your profiles an easy to recognise name, rather than just a number, you can create a text file on the root of your SD card called either "prof_n_i.txt" (for profiles stored in OSSC Pro's on-board flash) or "prof_n.txt" (for profiles stored on the SD card). Follow these steps to rename the profiles stored on the on-board flash.
1) Create a plain text file called "prof_n_i.txt" on your SD card. In Windows you can do this using the Notepad app, or any plain text editor (e.g NotePad++). In Linux you can use Vim or Nano. Since the file must be plain text, do not use a word processor or rich text editor like Word, Wordpad, Writer etc.
Remember that Windows can hide file extensions from the user when using file explorer and the default settings. Ensure the file is called "prof_n_i.txt" and not "prof_n_i" or even "prof_n_i.txt.txt"
2) Edit this file so that each line is the name of the profile. Terminate the line with a return. You can use a maximum of 17 characters per name
3) Ensure your edited file is saved to the to SD card. Safely remove the SD card from your computer and re-insert it into the OSSC Pro
4) Load the profile you want to rename, then immediately save it again to the same slot. Next time you recall the profile, you should see your custom name both on the character OLED display and on the on-screen menu.
To rename profiles stored on your SD card, you can create a file on the SD card called "prof_n.txt". The steps are then exactly the same as for renaming internal profiles.
Compatibility and special configuration
Most systems should work as-is without any special settings. Below is a list of tested systems and the ones which may require tweaking are shown in bold. We encourage the community to add sections under each system instead of having an enormous table here. That way we can have more detailed and specific information on a per system basis, and here links to all the systems tested so far.
Home consoles
- Atari Jaguar
- Microsoft Xbox
- Microsoft Xbox 360
- Microsoft Xbox Series X and Series S
- Nintendo 64
- Nintendo NES / Famicom
- Nintendo Gamecube
- Nintendo Super NES / Super Famicom
- Nintendo Wii
- Sega Dreamcast
- Sega Genesis / Mega Drive
- Sega Saturn
- SNK Neo Geo AES
- Sony PlayStation
- Sony PlayStation 2
Computers
Arcade Boards
- Capcom CPS-II
- Irem M72
- Sega System 16B
- SNK Neo Geo MVS
- Taito F3
- Taito FX-1B
- Toaplan V2
Basic downscaling for modern computers/consoles
The OSSC Pro is popular amongst classic CRT display users as a downscaler. Emulated games or modern pixel art titles can often be downscaled to a classic CRT display. How effective this process is depends on the base resolution of the game. For instance a game with 240p base resolution running at 720p on a console can take advantage of the OSSC Pros 3x line drop mode to be downscaled perfectly (since 240 x 3 = 720). The wiki page here lists a number of titles and their base resolutions.
While the unit has several output options to suit classic displays, for pixel perfect results the following modes can be used.
- 480p to 240p (2x line drop or scaler) - Equivalent to /2 prescale on the Morph for any title running at 480p.
- 720p to 240p (3x line drop or scaler) – Equivalent to /3 prescale on the Morph for any title running at 720p.
- 1080p to 240p (5x line drop or scaler) - Equivalent to /5 prescale on the Morph for any title running at 1080p.
Games that do not adhere to these specs (for instance the game Pocky and Rocky Re-shrined which has a 480x2270 base resolution and requires a /4 pre-scale at 1080p) can still be downscaled, but may not look good. For instance pixel heights may not be uniform or parts of the image may appear squashed, distorted or missing entirely. In these instances, use of 480i output mode may be preferable.
Remember that many modern pixel art titles run in widescreen. If your CRT is 4:3 aspect ratio and does not have aspect ratio correction, you will need to use scaler mode in order to convert the aspect ratio appropriately.
Wobbling Pixels Optimal Profiles
An optional package of pre-made profiles for the OSSC Pro has been created by user Wobbling Pixels. This package can be downloaded here and placed onto your SD card.
The profiles are designed for use when upscaling retro consoles, rather than downscaling or using a CRT. They are designed to get the sharpest possible image from the source material. Full instructions are provided in the link above.
Expansion cards and adapters
Extra AV output
Extra AV output card implements analog video output via VGA connector, analog audio outputs via 3.5mm jack and digital audio output via Toslink. At the moment video processing chain is identical to HDMI.
Several output video formats are supported and are listed below
- RGBHV
- RGsB
- RGBCS (TTL csync)
- SCART-RGB (via av_adapter)
- YPbPr from VGA or 3xRCA (via av_adapter)
Audio format support is summarized on table below
| Input | 3.5mm analog output | SPDIF output |
|---|---|---|
| AV1-3 analog | Y | (Y) |
| Toslink LPCM2.0 | (Y) | Y |
| Toslink DD5.1/DTS | N | Y |
| HDMI LPCM2.0 | Y | (Y) |
| HDMI LPCM7.1 | Y (front 2ch only) | (Y) (front 2ch only) |
| HDMI DD5.1/DTS | N | Y |
Y=yes, (Y)=supported via future fw update, N=no
Legacy AV input
Legacy AV input card adds support for composite, S-video and RF. RF support is work in progress and is not guaranteed to produce clean video with all sources. Supported video formats include PAL, PAL60, NTSC and NTSC50 (?).
Audio from composite and s-video sources need to be connected to AV2 RCA inputs as cost of the board is kept at minimum. The video is digitized with a dedicated cvbs/s-video decoder chip which has more limited configurability with regards to sync processing and sampling (e.g. no optimal timings supported). A dedicated list of processing options related to cvbs/s-video/rf decoding is found under Expansion opt -> Legacy AV opt.
To scan for RF source, launch "RF chscan (2min)" with correct TV standard from the menu. Wait until the scan has finished (which happens if a channel is found or end of the range is reached). The RF input can be now selected. The channel tuning settings are included when a profile is saved/loaded.
AV adapter
A custom AV input/output adapter (shown below) can be used to connect
- VGA or component input sources into SCART input
- SCART-RGB or component input sources into VGA input
- VGA output of Extra AV output expansion card into the adapter, providing SCART-RGB or 3xRCA YPrPb output instead
A fully wired SCART (or VGA) cable needs to be connected between the adapter and OSSC Pro (or Extra AV output) board to fully support all above use cases. Design and gerbers are available here. Pre-assembled adapters are also sold by VGP. Latest version (1.3) of the adapter has 2 switches to make it as compatible with different configurations where SCART is involved:
SW1 - sync routing:
- SCART_O: Select this setting when using the board to output video to SCART TV via Extra AV output expansion. A fully wired VGA cable is required (including pins 4 and 9) to pass sync and RGB status voltage to the TV. If pin 4 is not wired (or is grounded), SCART_I setting can be used as a backup where sync is routed from voltage divider instead of proper 75ohm driver.
- SCART_I: Use this setting when connecting SCART-RGB source to VGA input of Pro. Pin 4 of the VGA cable must be wired in this use case, but pin 9 does not matter.
SW2 - audio routing:
- SCART_O: Select this setting when using the board to output audio to SCART TV via Extra AV output expansion.
- SCART_I: Use this setting when connecting audio from SCART source into AV2 3.5mm input of Pro.
Firmware update
Firmware is updated via microSD card. Download .bin file for the latest release from github and:
Option 1) Rename it as ossc_pro.bin and place it to root of FAT32-formatted SD card.
Option 2) (Supported if running fw >= 0.78) Place it into "fw" folder on FAT32 or exFAT formatted SD card.
Launch upgrade via Settings menu. The device enters standby mode when update is finished. If you get an error code during update, refer here
Firmware update via JTAG
Firmware can also be updated via the JTAG connector and a suitable programmer such as the terasIC USB Blaster. A tutorial on how to do this is available here.
Firmware changelog and roadmap
v0.81
- Robustness fixes
- SD card corruption and freezing issues resolved
- Csync output AND-type implementation added as default
- ADV7280 comb filter config setting corrected
- Support for custom Lumacode palettes added
Older versions
v0.80
- 384p and 768i CRT output presets added
- Legacy AV options expanded
- minor fixes related to audio metadata refresh and picture position adjustment
v0.79
- support for 24Hz HDMI sources added
- support for higher framelock/BFI multipliers added
- “720p max” EDID preset added
- Full TX setup compatibility option added
- various robustness and timing improvements
- Lumacode support for Atari GTIA and Atari VCS added
v0.78
- 1920x1440@60 input support added for both analog and digital sources
- 1152x864_75 sampling preset added
- 2048x1536 and 2560x1920 (PR2x) output presets added
- LG VRR compatibility fixed
- Workaround for Mister SNES core jitter added
- Scaler framelocking consistency improved
- Support for RF added (legacy AV expansion)
- UI improvements
- infoscreen display when OSD is off
- OSD highlight color option
- Profile number entry via remote
- FW file selection menu
v0.77
- new features added for HDMI frontend
- EDID presets and custom EDID option
- pixel decimation by FPGA (previously RX de-repetition)
- new features added for SDP frontend
- audio source selection
- CTI options
- 1080p line drop modes added
- signal info display option added into menu
v0.76
- Lumacode support added
- New line drop modes added
- Custom scl_alg/shmask loading improved
- Shadow mask strength adjustment option added
- 10bit coefficient support added for scaling algorithms
- Power-up state option added
- Added support for exFAT
- Fixed number of minor bugs
- SPDIF output active when power off
- random bobbing with analog HV sync sources when sync edges are closely aligned
- Garbage on topmost line with LM Bob deinterlace
- 0x00/0xff extreme RGB values clamped with HDMI input
- scanline issues on 2160p mode
v0.75
- added support for Legacy AV in expansion
- added support for YPbPr output via extra_av_out expansion
- added support for custom EDID on HDMI RX
- added VRR flag (Freesync) option
- enabled customization of frame-unlock mode refresh rate
- improved audio output compatibility
- various small bug fixes
v0.74
- number of PAL console presets added
- generic sampling rate preference option added
- display output timing editor added
- PSP sampling preset added
v0.72/0.73
- fix GBI presets
- store size/position adjustments for HDMI inputs as well
- add 2880x2160_60 preset option
- enable 2880x2160 mode for 240p/288p A-LM
- support direct video "DV1" mode from Mister and PixelFX products
- sync processing fixes for Taito F3 etc.
v0.71
- fix audio source selection with HDMI RX
- fix size/position adjustment vertical limit
- add support for defining profile names via text file
- improve 1080p120 compatibility
v0.70
- Fix HDMI TX/RX related issues
v0.69
- Initial release
Scheduled improvements
- Lower scaler mode latency
- Rotation